ApoBrite™ U470 caspase 3/7 substrate
Cell-Permeable
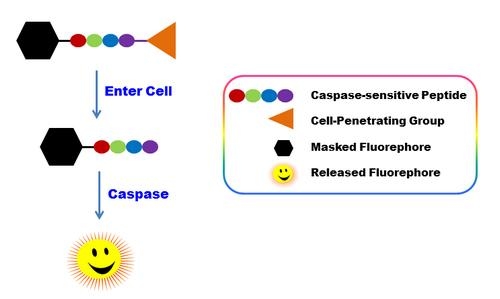
ApoBrite™ U470 is our recently developed cell-permeable fluorogenic caspase substrate, the first fluorogenic probe for the direct detection of caspase activities in live cells. ApoBrite U470 consists of three moieties including a). masked fluorophore, b). caspase-selective peptide fragment (DEVD), and c). cell-penetrating moiety. The cell-penetrating moiety carries the probe into live cells. Upon entering live cells the caspase-selective peptide fragment is cleaved by a caspase to release the masked fluorophore. The intensity of recovered fluorescence is directly related to the activity of caspase to be measured. Compared to the existing caspase assays in live cells, ApoBrite™ U470 is much more robust, convenient and accurate. It does not need a DNA interaction to be fluorescent as reported for NucView reagents. It does not inhibit caspase activity as reported for the FMK peptide probes. Although fluorescent FMK peptide inhibitors of caspases are widely used for detecting caspase activities in live cells, this technology has a few severe limitations: a). FMK caspase inhibitors have high cytotoxicity since FMK peptides bind covalently to active caspases; b). The irreversibly covalent binding of FMK peptides to caspases inhibits caspase activities, causing false positive apoptosis; c). FMK assays have extremely high background, and require intensive washings, resulting in very low through put; d). FMK peptides are not stable in aqueous solutions, and have to be used immediately.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20200 | 100 Tests | Price |
Physical properties
| Solvent | DMSO |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on July 12, 2023
