C-PC
C-Phycocyanin; CAS 11016-15-2
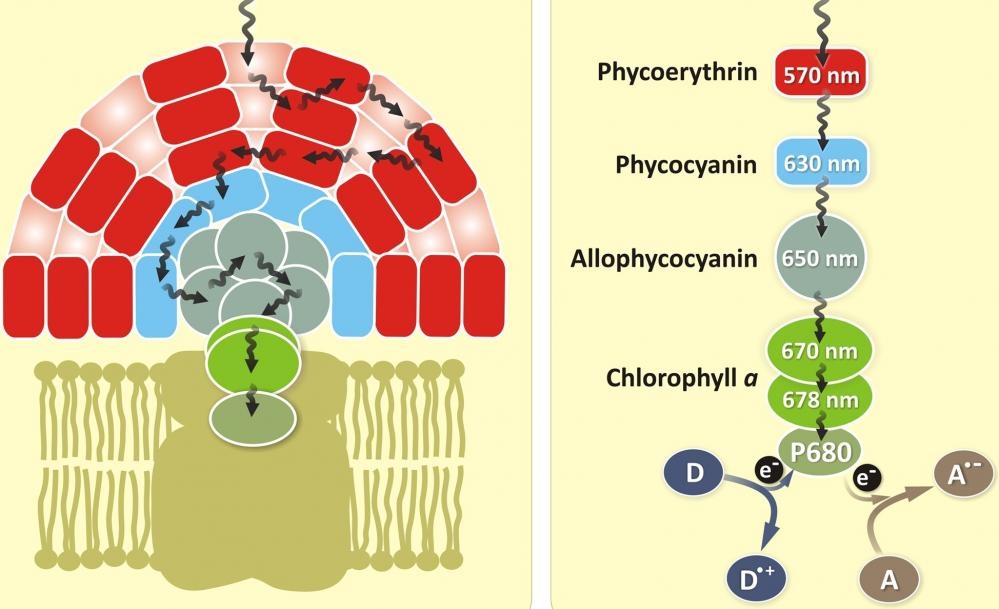
C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) occurs as the major phycobiliprotein in many cyanobacteria and as a secondary phycobiliprotein in some red algae. The pigment has a single visible absorption maximum between 615 and 620 nm and a fluorescence emission maximum at ~650 nm. Its molecular weight is between 70,000 and 110,000 daltons. The pigment is composed of two subunits, ? and ?, which occur in equal numbers, but the exact number of ? and ? pairs which make up the molecule may vary among the species. Both ? and ? subunits contain only the PCB chromophore. In addition to absorbing light directly, this intensely blue pigment accepts quanta from phycoerythrin by fluorescence energy transfer in organisms in which PE is present. The red fluorescence of C-PC is transferred to allophycocyanin.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2553 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | ~264,000 |
| Solvent | Water |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Refrigerated (2-8 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
| CAS | 11016-15-2 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 18, 2026
