Calbryte™ 590 AM
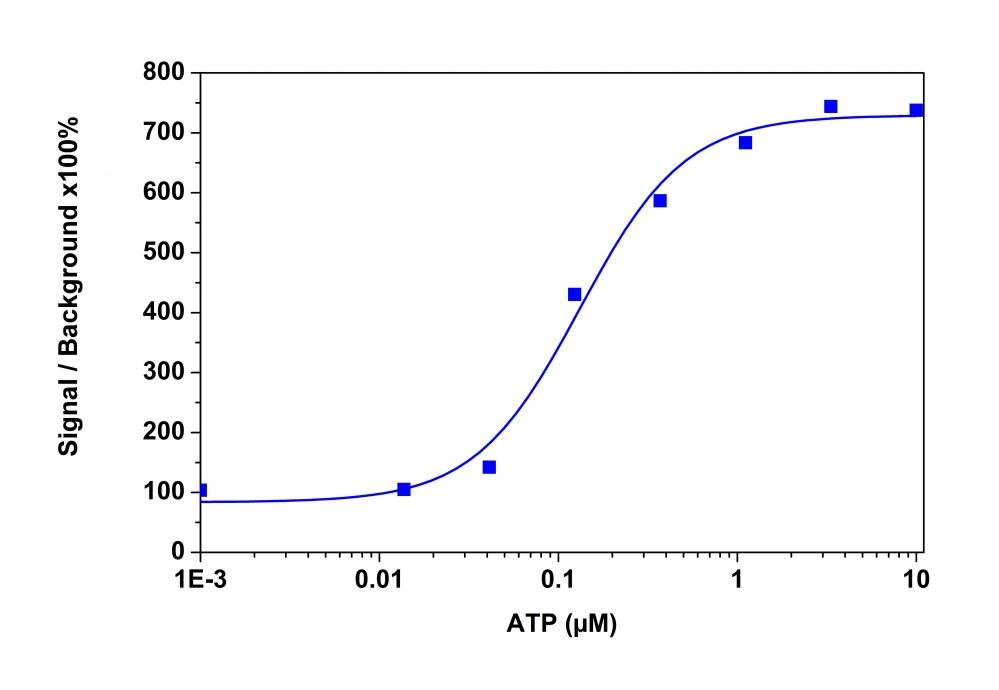
The intracellular calcium flux assay is a widely used method in monitoring signal transduction pathways and high throughput screening of G protein"coupled receptors (GPCRs) and calcium channel targets. Followed by Rhod-2 being introduced in 1989, Rhod-4 and Cal-590 were later developed with improved signal/background ratio, and they became the widely used red fluorescent Ca2+ indicators for confocal microscopy, flow cytometry and high throughput screening applications. In CHO and HEK cells Rhod-4 and Cal-590 have cellular calcium response that are 10 times more sensitive than Rhod-2 AM. However, Cal-590 and Rhod-4 are still less sensitive to calcium in cells than the corresponding green fluorescent calcium indicators (e.g., Fluo-8® and Cal-520®). Calbryte™ 590 is a new generation of red fluorescent indicators for the measurement of intracellular calcium. Its greatly improved signal/background ratio and intracellular retention properties make Calbryte™ 590 AM the most robust red fluorescent indicator for evaluating GPCR and calcium channel targets as well as for screening their agonists and antagonists in live cells. Like other dye AM cell loading, Calbryte™ 590 AM ester is non-fluorescent and once gets inside the cell, it is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterase and gets activated. The activated indicator is a polar molecule that is no longer capable of freely diffusing through cell membrane, essentially trapped inside cells.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20700 | 2x50 ug | Price | |
| 20701 | 10x50 ug | Price | |
| 20702 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Dissociation constant (Kd, nM) | 1400 |
| Molecular weight | 1218.77 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 581 |
| Emission (nm) | 593 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | TRITC/Cy3 |
| Emission | TRITC/Cy3 |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 540 |
| Emission | 590 |
| Cutoff | 570 |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode/Programmable liquid handling |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 25, 2026

