Amplite® Colorimetric Calcium Quantitation Kit
Blue Color
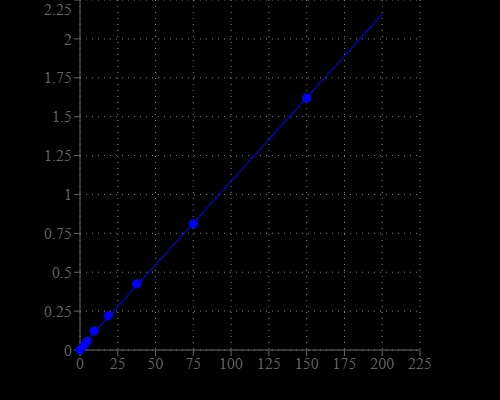
Calcium is essential for all living organisms, particularly in cell physiology, where movement of the calcium ion Ca2+ into and out of the cytoplasm functions as a signal for many cellular processes. Calcium is the fifth most abundant element by mass in the human body, where it is a common cellular ionic messenger with many functions, and serves also as a structural element in bone. Calcium plays an important role in mediating the constriction and relaxation of blood vessels, nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. The serum level of calcium is closely regulated within a fairly limited range (9 to 10.5 mg/dL) in the human body. Both hypocalcaemia and hypercal caemia are serious medical disorders. Causes of low calcium levels include chronic kidney failure, vitamin D deficiency, and low blood magnesium levels that can occur in severe alcoholism. Amplite® Calcium Detection Kit provides a simple method for detecting calcium in physiology solutions. This kit uses our Calcium Blue™ as the chromogenic calcium indicator. Its absorbance changes in response to calcium binding. Calcium Blue™ binds calcium tightly in the neutral pH range, generating Calcium Blue™-calcium complex that has intense absorption at ~650 nm.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36361 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Absorbance microplate reader | |
| Absorbance | 600 or 650 nm |
| Recommended plate | Clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026
