Amplite® Colorimetric Oxaloacetate Assay Kit
Red Color
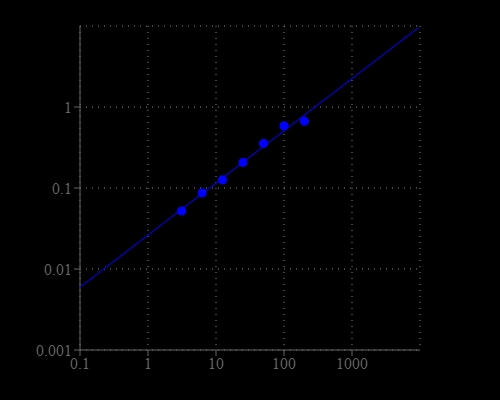
Oxaloacetate is an important part of citric acid cycle, where it reacts with Acetyl-CoA to form citrate. It is also involved in gluconeogenesis, urea cycle, glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, and fatty acid synthesis. The lack of oxaloacetate limits gluconeogenesis and urea cycle function, and can lead to decreased production of energy. Oxaloacetate can be also used as blood glutamate scavengers to provide neuroprotection after traumatic brain injury, expressed both by reduced neuronal loss in the hippocampus and improved neurologic outcomes. Amplite® Colorimetric Oxaloacetate Assay Kit offers a sensitive assay for quantifying oxaloacetate in biological samples. Oxaloacetate is converted to pyruvate that generates hydrogen peroxide through an enzyme coupled reaction. The production of hydrogen peroxide is monitored with Amplite® Red by an absorbance microplate reader at 575 nm.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13840 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Absorbance microplate reader | |
| Absorbance | 575 nm |
| Recommended plate | Clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 4, 2026
