Amplite® Fluorimetric cADP-Ribose Assay Kit
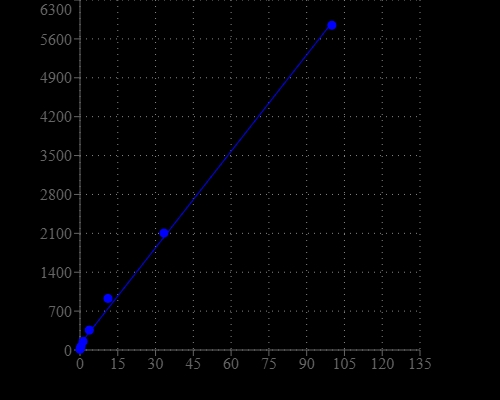
cADP-ribose (cADPR) is a novel Ca2+ messenger derived from NAD+. ADP-riboxyl cyclase (ADPRC) catalyzes the synthesis of cADPR from NAD+, but the reaction can be reversed in the presence of high concentration of nicotinamide, producing NAD+ from cADPR stoichiometrically. The resultant NAD+ can be detected using our newly developed NAD sensor Quest Fluor™ NAD reagent. This makes monitoring cADPR in tissues and cell cultures possible in the low nM range. The NAD+ detection using Quest Fluor™ NAD reagent is specific to NAD+ and has no reaction to NADH. The fluorescent signal can be readily detected. This assay can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microtiter plate.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20305 | 100 tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 420 nm |
| Emission | 480 nm |
| Cutoff | 435 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 8, 2026
