Amplite® Fluorimetric Fluorescamine Protein Quantitation Kit
Blue Fluorescence
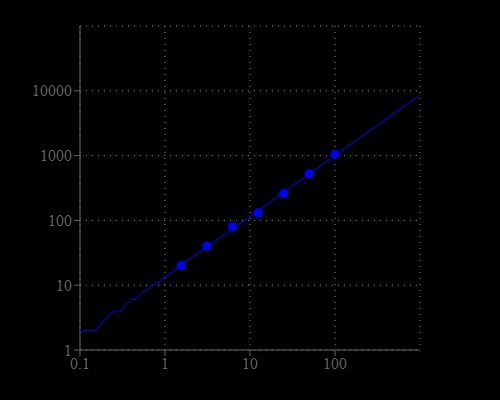
Fluorescamine is intrinsically non-fluorescent but reacts rapidly with primary aliphatic amines, including those in peptides and proteins, to yield a blue-green-fluorescent derivative. The Amplite® fluorescamine protein assay kit provides a simple method for quantifying protein concentration in solutions. This Amplite® fluorescamine protein assay kit can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microtiter-plate format and easily adapted to automation with no separation steps required. The assay can be completed within 30 minutes. With the Amplite® fluorescamine protein assay kit, as little as 3 ug/mL of BSA can be detected.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11100 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 380 |
| Emission | 470 |
| Cutoff | 420 |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 27, 2026
