Amplite® Fluorimetric Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Assay Kit
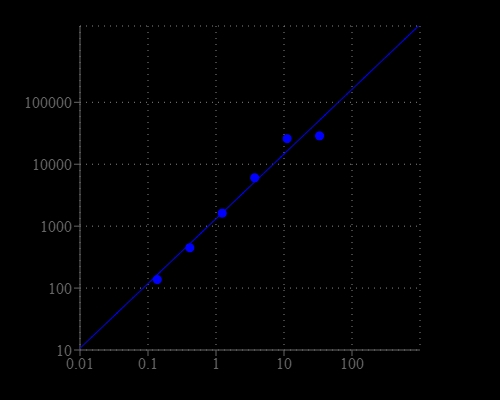
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphoglucono-Δ-lactone, the first and rate-limiting step in the pentose phosphate pathway. It is critical metabolic pathway that supplies reducing energy to cells (such as erythrocytes) by maintaining the level of co-enzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), and for the production of pentose sugars. The production of NADPH is of great importance for tissues actively engaged in biosynthesis of fatty acids and/or isoprenoids, such as the liver, mammary glands, adipose tissue, and the adrenal glands. The NADPH also maintains the level of glutathione in these cells that helps protect the red blood cells against oxidative damage. Deficiencies in G6PD predispose individuals to non-immune hemolytic anemia. AAT Bioquest's Amplite® Fluorimetric Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Assay Kit provides a simple, sensitive and rapid fluorescence-based method for detecting G6PD in biological samples such as serum, plasma, urine, as well as in cell culture samples. In the enzyme coupled assay, G6PD activity is proportionally related to the concentration of NADPH that is specifically monitored by a fluorogenic NADPH sensor to yield a highly red fluorescence product. The fluorescence signal can be read with a fluorescence microplate reader. With the G6PD assay kit, we were able to detect as little as 1 mU/ml G6PD in a 100 µL reaction volume.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13806 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 540 nm |
| Emission | 590 nm |
| Cutoff | 570 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026
