Amplite® Fluorimetric Lead (II) Ion Quantitation Kit
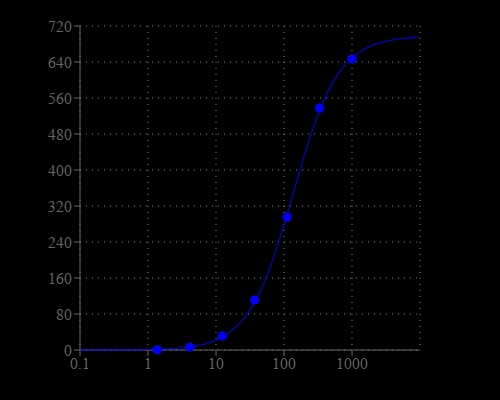
Lead is a highly poisonous metal to human beings, especially young children. Lead interferes with cell signaling and gene expression, causing severe damages to the brain, liver, kidney, and even death. Because of its long history in mining and smelting, as well as widespread use in battery, paint and gasoline, lead pollution in soil and groundwater has been one of the most serious environmental problems. Amplite® Fluorimetric Lead (II) Ion Quantitation Kit provides a robust method for detecting lead (II) ion in solution. It uses Lead Green™, a selective and sensitive green fluorescence probe that can be easily monitored with a fluorescence microplate reader (Ex/Em = 490/530 nm). The Amplite® Fluorimetric Lead (II) Ion Quantitation Kit can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microplate format and easily adapted to automation with no separation steps required. The assay can be completed within 30 minutes. With the Amplite® Fluorimetric Lead (II) Ion Quantitation Kit, as little as 4µM lead (II) ion was detected.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 19007 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm |
| Emission | 530 nm |
| Cutoff | 515 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 4, 2026
