Cal-670™-Dextran Conjugate
MW 3,000
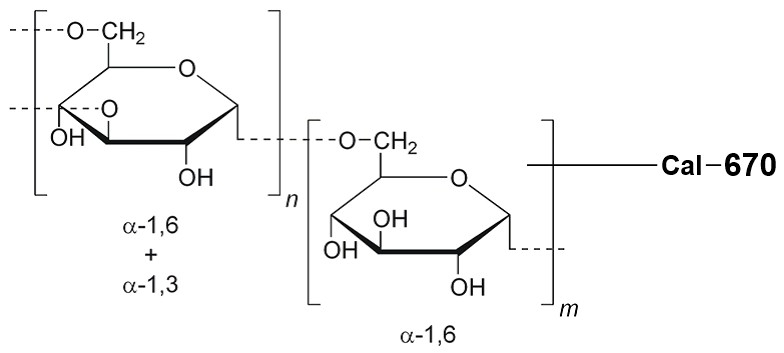
Calcium measurement is critical for numerous biological investigations. Fluorescent probes that show spectral responses upon binding calcium have enabled researchers to investigate changes in intracellular free calcium concentrations by using fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microplate readers. Cells may be physically loaded with the cell-impermeant salt forms of these dextran-conjugated calcium indicators using patch pipette or microinjection. The fluorescence signal from these cells is measured using fluorescence microscopy. The dextran forms of our calcium indicators show a dramatic reduction in both leakage and compartmentalization compared to the AM ester forms. Among the fluorescent red calcium indicator dextran conjugates, Cal-670 dextran conjugates might be a better choice than other red fluorescent dextrtan conjugates due to its longer fluorescence wavelength optimized for in vivo imaging. Cal-670™ is a near infrared (NIR) calcium indicator with maximum emission at ~675 nm. It can be well excited with the red lasers at 633 nm or 647 nm. Cal-670™ is one of the very few calcium indicators that can be potentially used for in vivo imaging since it has a NIR fluorescence.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20456 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | ~5000 |
| Solvent | Water |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 667 |
| Emission (nm) | 680 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

