Cell Meter™ APC-Annexin V Binding Apoptosis Assay Kit
Optimized for Flow Cytometry
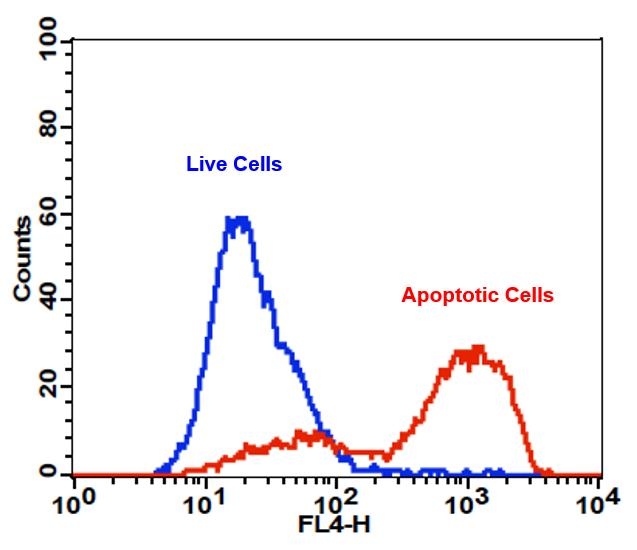
Annexin V may be conjugated to fluorochromes including APC. This format retains its high affinity for phosphatidylserine (PS) and thus serves as a sensitive probe for flow cytometric analysis of cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Since externalization of PS occurs in the earlier stages of apoptosis, APC Annexin V staining can identify apoptosis at an earlier stage than assays based on nuclear changes such as DNA fragmentation. APC Annexin V staining precedes the loss of membrane integrity which accompanies the latest stages of cell death resulting from either apoptotic or necrotic processes. Therefore, staining with APC Annexin V is typically used in conjunction with a vital dye such as propidium iodide (PI) or 7-Amino-Actinomycin (7-AAD) to allow the investigator to identify early apoptotic cells.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22837 | 100 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.195 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 730000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 651 |
| Emission (nm) | 660 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Refrigerated (2-8 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 640 nm laser |
| Emission | 660/20 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | APC channel |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on October 8, 2024

