Cell Meter™ Beta-Arrestin Translocation GPCR Signaling Kit
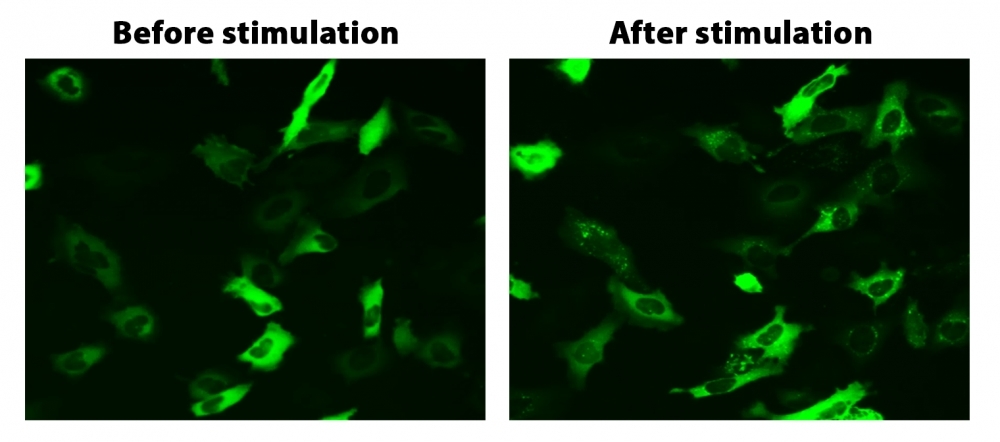
Virtually all G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) rapidly undergo desensitization by a common pathway upon activation by ligand binding. The binding of beta-arrestin, a cytoplasmic protein, to an activated receptor deactivates the GPCR signaling and initiates the translocation of the receptor into the cell where the ligand is removed, and the receptor is recycled back to the cell membrane. By attaching a fluorescent label, such as GFP, to beta-arrestin, the location of the receptor arrestin complex can be monitored. Since desensitization only occurs with an activated receptor, monitoring beta-arrestin translocation and subsequent receptor recycling provides a reliable method to detect the activation of a GPCR target. Cell Meter™ Beta-Arrestin translocation GPCR Signaling Kit provides a powerful functional assay to screen activities of target compounds against known or orphan GPCR targets via fluorescence imaging. The activation of the targeted GPCR induces the translocation of the fluorescence to the cell membrane and/or to endocytic vesicles.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36390 | 100 Tests | Price | |
| 36391 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter set |
| Emission | FITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026
