Cell Meter™ BX520 fixable viability dye
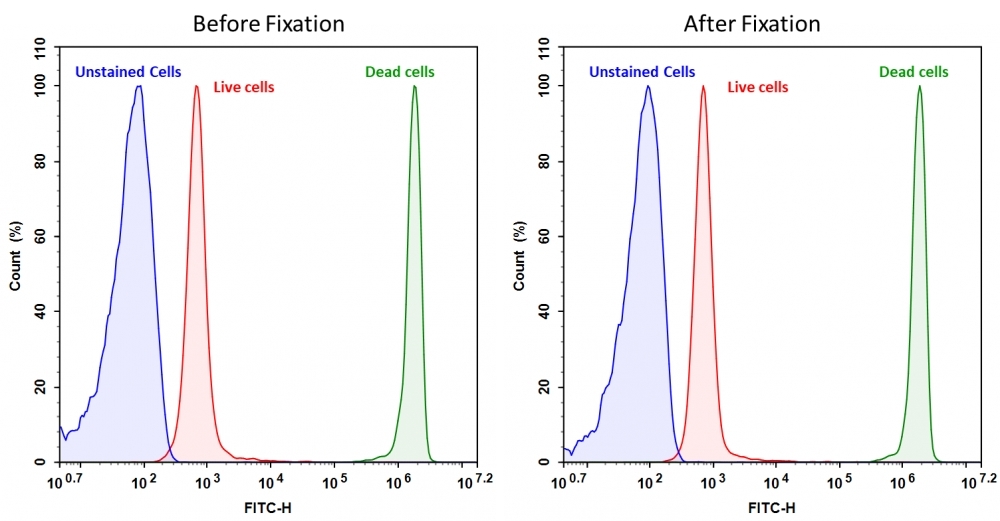
Discrimination and exclusion of dead cells from live cells allows cleaner separation and identification of cell populations. Cell Meter™ fixable viability dyes are a large family of cell-impermeable fluorescent viability dyes that are optimized to match the major excitation lasers of common flow cytometers, such as 350, 405, 488, 633 and 647 nm. These dyes are impermeant to live cells but permeant to cells with compromised membranes. They irreversibly react with amine- and thiol-containing proteins and other cellular components. Since dead or fixed cells with a compromised membrane more readily react with Cell Meter™ fixable cell stains, thus stain brighter than live cells with an intact membrane, these dyes can be used to assess live vs. dead status of mammalian cells. There are a few factors to be considered when using these dyes, e.g., the titration of each dye to ensure that live cells have minimal to no staining. Cell Meter™ BX520 fixable cell stain is optimized to be excited with the blue laser at 488 nm with emission at 520 nm (FITC channel). Compared to other commercially similar viability dyes, this fixable viability dye is much more robust and stable.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22510 | 200 Tests | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 881.76 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 491 |
| Emission (nm) | 516 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC filter set |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter set |
| Emission | FITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 24, 2026

