Cell Meter™ Live Cell TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence
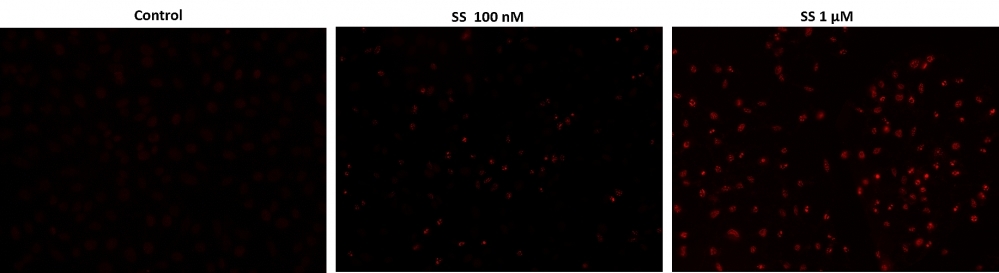
DNA fragmentation represents a characteristic of late stage apoptosis. DNA fragmentation in apoptotic cells can be detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL). The TUNEL assay relies on the presence of nicks in the DNA which can be identified by TdT, an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of dUTPs that are secondarily labeled with a marker. All the existing TUNEL assays contain the highly toxic sodium cacodylate which might induces apoptosis and also decrease DNA production and DNA strands. Our Cell Meter™ TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit uses proprietary buffer system free of sodium cacodylate. The kit is based on the incorporation of our unique proprietary fluorescent dye into the DNA fragments that form during apoptosis. The assay is optimized for the direct detection of apoptosis in either detached or attached cells without using antibody. The kit provides all the essential components with an optimized assay protocol. It is suitable for fluorescence microplate reader, fluorescence microscope, or flow cytometer.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22844 | 50 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 27500 |
| Excitation (nm) | 549 |
| Emission (nm) | 648 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 660/20 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | PE-Cy5 channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | TRITC filter |
| Emission | TRITC filter |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on October 8, 2024

