Cell Meter™ Mitochondrion Membrane Potential Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence Optimized for Flow Cytometry
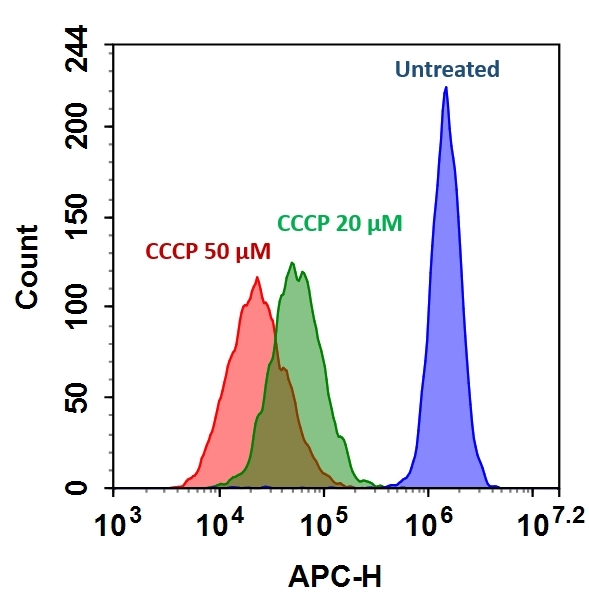
Our Cell Meter™ assay kits are a set of tools for monitoring cell viability. There are a variety of parameters that can be used. This particular kit is designed to detect cell apoptosis by measuring the loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). The collapse of MMP coincides with the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pores, leading to the release of cytochrome C into the cytosol, which in turn triggers other downstream events in the apoptotic cascade. Our Cell Meter™ Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit provides all the essential components with an optimized assay method. This fluorimetric assay uses our proprietary cationic MitoTell™ Red for the detection of apoptosis in cells with the loss of MMP. In normal cells, the red fluorescence intensity is increased when MitoTell™ Red is accumulated in the mitochondria. However, in apoptotic cells, the fluorescence intensity of MitoTell™ Red decreases following the collapse of MMP. Cells stained with MitoTell™ Red can be visualized with a flow cytometer at APC or Cy5 channel. The kit is optimized for screening apoptosis activators and inhibitors with a flow cytometer.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22806 | 100 tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 613 |
| Emission (nm) | 631 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 640 nm laser |
| Emission | 660/20 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | APC channel |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

