Cell Meter™ Phosphatidylserine Apoptosis Assay Kit
Blue Fluorescence Optimized for Microplate Readers
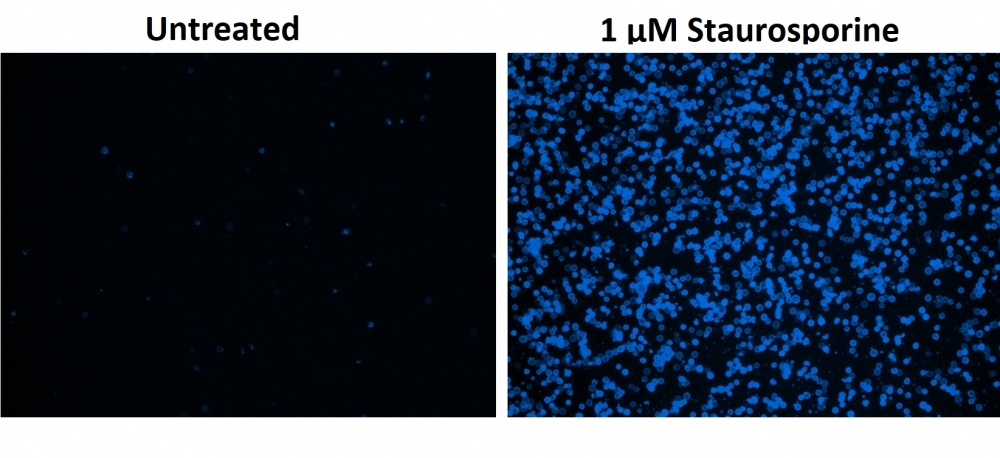
Our Cell Meter™ assay kits are a set of tools for monitoring cell viability. There are a variety of parameters that can be used for monitoring cell viability. This particular kit is designed to monitor cell apoptosis through measuring the translocation of phosphatidylserine (PS). In apoptosis, PS is transferred to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. The appearance of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface is a universal indicator of the initial/intermediate stages of cell apoptosis and can be detected before morphological changes can be observed. This particular kit is designed to monitor cell apoptosis through measuring the translocation of phosphatidylserine (PS). This kit uses our proprietary fluorescent small molecule-based Apopxin™ PS sensor that specifically binds PS with affinity much higher than Annexin V (Kd < 10 nM). It has blue fluorescence upon binding to membrane PS. It can be used in the formats of microplate, microscope and flow cytometer while most of other commercial apoptosis assay kits are only used with either microscope or flow cytometry platform.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22790 | 100 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 405 nm |
| Emission | 450 nm |
| Cutoff | 420 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 4, 2026
