Cell Navigator® Exosome Fluorescence Staining Kit
Orange Fluorescence
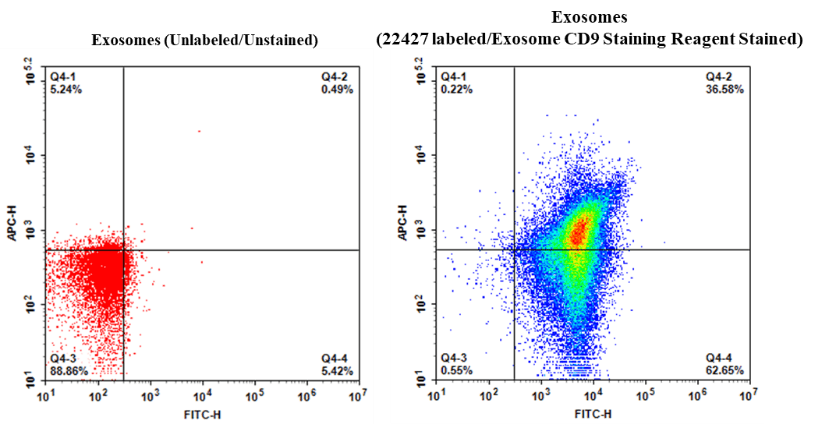
Cell Navigator® Exosome Fluorescence Staining Kit (Orange Fluorescence) is a reliable tool for labeling extracellular vesicles with Exsomight™ Orange dye for clear, low-background detection in fNTA, flow cytometry, and fluorescence microscopy.
- Minimized aggregation and background: Enhances solubility to reduce dye clustering and non-specific fluorescence
- Efficient EV membrane integration: Provides uniform labeling with high signal fidelity and minimal off-target staining
- Applications: Ideal for EV population analysis, cellular uptake studies, and high-resolution imaging
- Comparable alternative: Offers a comparable option to PKH26-based EV labeling kits from Sigma-Aldrich with reduced aggregation and improved detection accuracy

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22427 | 100 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 6, 2026
