Cell Navigator® F-Actin Labeling Kit
Green Fluorescence
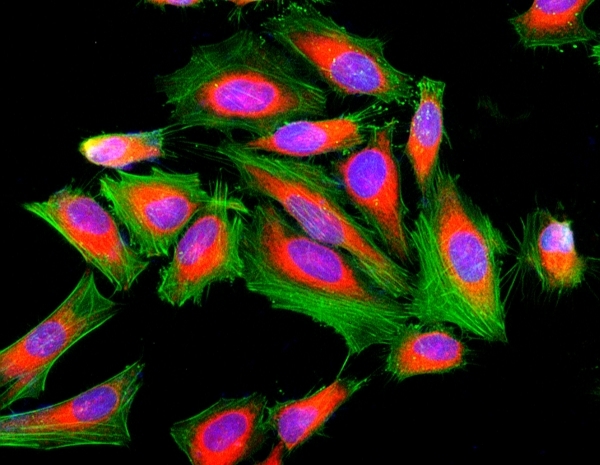
Our Cell Navigator® fluorescence imaging kits are a set of fluorescence imaging tools for labeling sub-cellular organelles such as membranes, lysosomes, mitochondria and nuclei etc. The selective labeling of live cell compartments provides a powerful method for studying cellular events in a spatial and temporal context. This particular kit is designed to label F-actins of fixed cells in green fluorescence. The kit uses a green fluorescent phalloidin conjugate that is selectively bound to F-actins. This green fluorescent phalloidin conjugate is a high-affinity probe for F-actins with much higher photostability than the fluorescein-phalloidin conjugates. Used at nanomolar concentrations, phallotoxins are convenient probes for labeling, identifying and quantitating F-actins in formaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized tissue sections, cell cultures or cell-free experiments. The labeling protocol is robust, requiring minimal hands-on time. The kit provides all the essential components with an optimized staining protocol.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22661 | 500 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.21 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.11 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 75000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 491 |
| Emission (nm) | 516 |
| Quantum yield | 0.9 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter |
| Emission | FITC filter |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 20, 2026

