CytoCalcein™ Violet 500
Excited at 405 nm
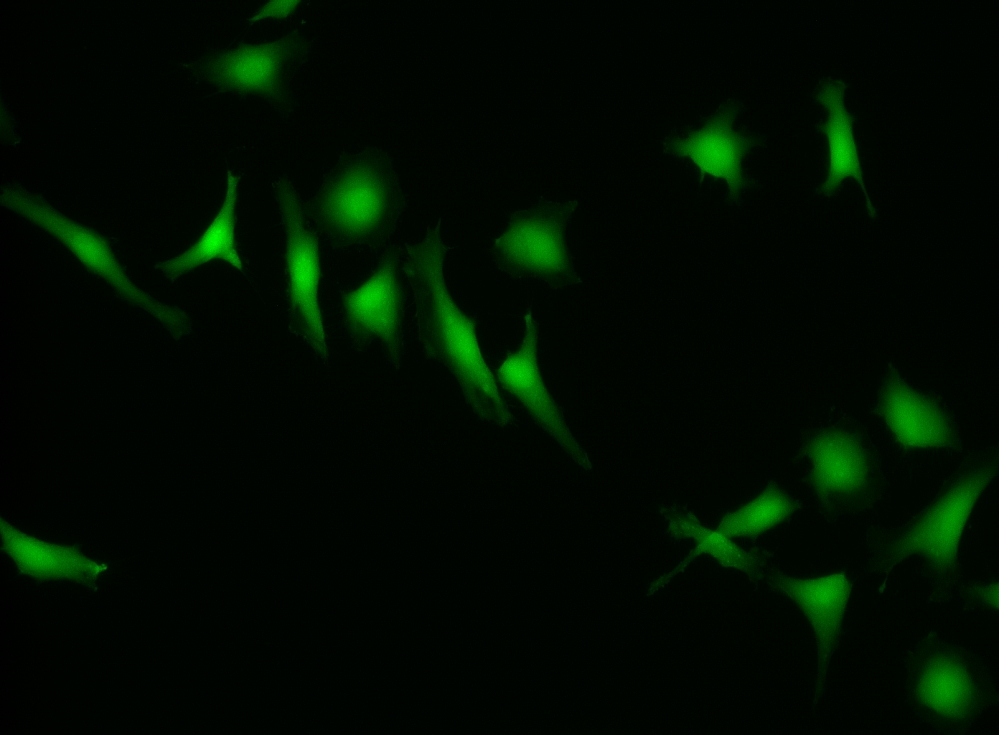
CytoCalcein™ Violet 500 is designed for labeling live cells in the same way to calcein, AM. It has a maximum excitation at 405 nm, which perfectly matches the violet laser line equipped in most flow cytometers, and it is well-excited by the excitation sources of fluorescence microscopes. Upon getting into live cells the weakly fluorescent CytoCalcein™ Violet 500 is hydrolyzed into a strongly fluorescent dye that has an excitation/emission maxima of 405/500 nm. This exceptional spectral separation from the typical FACS fluorophores provides additional options for multiplexing experiments. CytoCalcein™ Violet 450 and CytoCalcein™ Violet 500 have been developed for flow cytometric applications. CytoCalcein™ dyes exhibit similar biological properties to calcein, AM. They are optimized for the excitation wavelengths of a variety of flow cytometers, providing additional colors for flow cytometric analysis of live cells. CytoCalcein™ Violet 450 and CytoCalcein™ Violet 500 are well excited by 405 nm of violet laser and emit fluorescence at 450 nm and 500 nm respectively.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22013 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 517.93 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 420 |
| Emission (nm) | 505 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 405 nm laser |
| Emission | 525/40 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | AmCyan channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | DAPI filter set |
| Emission | DAPI filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 405 |
| Emission | 500 |
| Cutoff | 475 |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

