MycoLight™ Flow Cytometric Live Bacteria Assay Kit
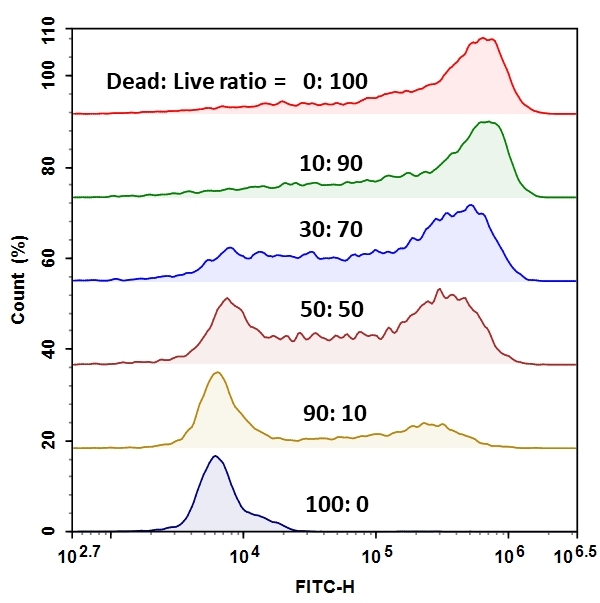
The MycoLight Flow Cytometric Live Bacteria Assay Kit provides an easy and convenient methodfor evaluating bacterial vitality as a function of the intracellular esterase activity. MycoLight™ 520 is non-fluorescent esterase substrate that diffuse into both Gram positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Upon hydrolysis by bacterial intracellular non-specific esterase, a green fluorescent product is produced and accumulated within bacteria. Compared to the commonly used esterase substrate CFDA and CFDA-AM, this kit provides brighter and more stable signal with lower background and easier staining protocol.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22407 | 100 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.31 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.12 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 76000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 498 |
| Emission (nm) | 526 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC channel |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 6, 2026

