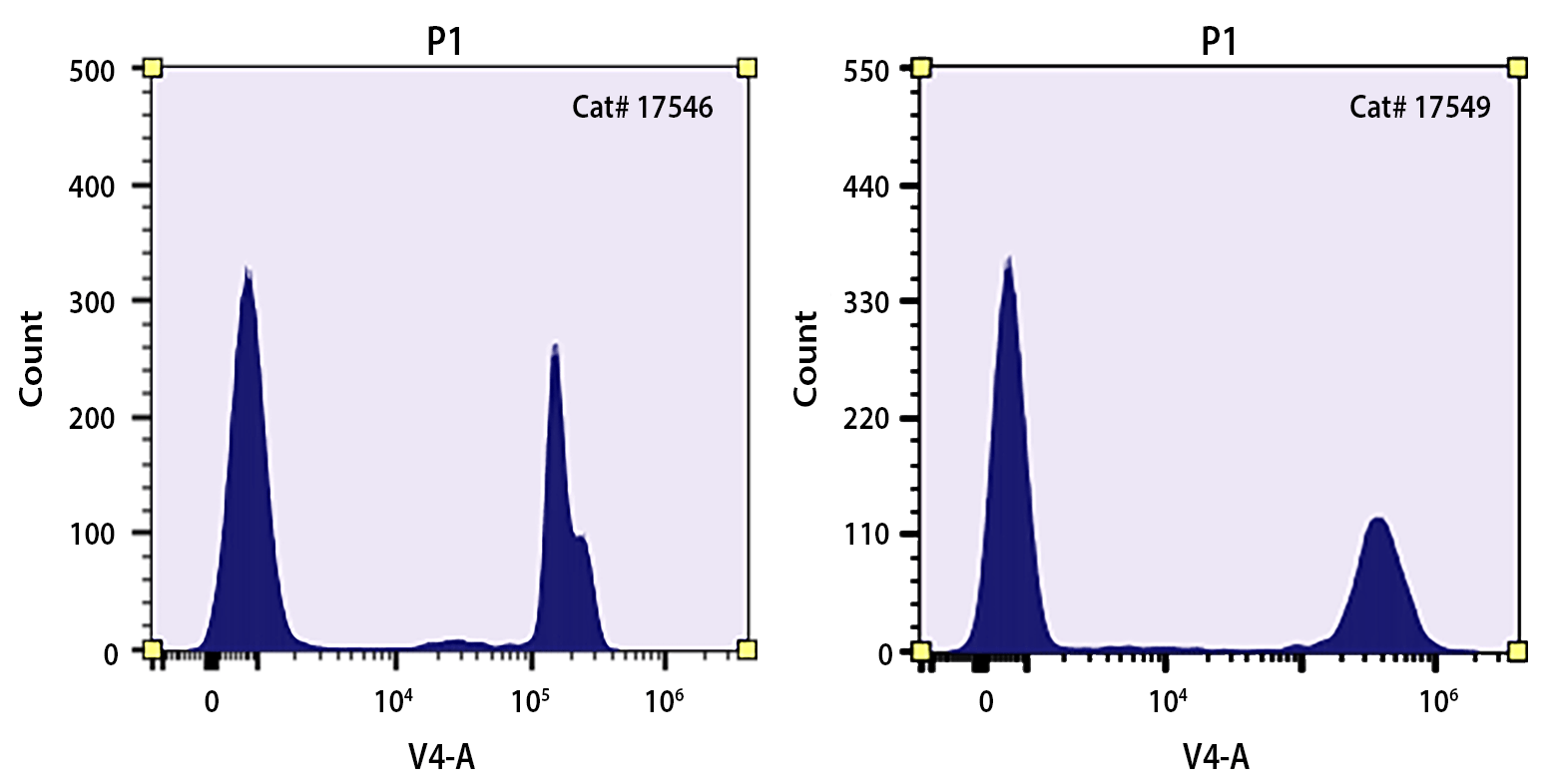
Nuclear Blue™ DCS2 is the same molecule to SYTOX™ Blue Dead Cell Stain (SYTOX™ is a trademark of ThermoFisher). Nuclear Blue™ DCS2 is a simple and quantitative single-step dead-cell indicator for use with violet laser equipped flow cytometers. It is a high-affinity nucleic acid stain that easily penetrates cells with compromised plasma membranes but will not cross uncompromised cell membranes. Under the same conditions, our Nuclear Violet™ DCS1 (#17549) gives much higher signal/background ratio than SYTOX™ Blue Dead Cell Stain. Nuclear Violet™ DCS1 is better excited by the violet laser at 405 nm than SYTOX™ Blue Dead Cell Stain. After brief incubation with Nuclear Violet™ DCS1 stain, the nucleic acids of dead cells fluoresce bright blue when excited with 405 nm violet laser light. The violet-excited fluorescence emission of Nuclear Violet™ DCS1 stain permits clear discrimination from probes excited by most other laser lines, facilitating the development of multicolor assays with minimal spectral overlap between signals.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17546 | 0.5 ml | Price | |
| 17547 | 1 ml | Price |
| Molecular weight | 668.36 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
| Excitation (nm) | 445 |
| Emission (nm) | 470 |
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 405 nm Laser |
| Emission | 473/15 nm Filter |
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |

