PE-iFluor® 594 Tandem
PE-iFluor® 594 Tandem is a high-performance tandem fluorophore combining R-phycoerythrin with iFluor® 594, providing bright, photostable emission for flow cytometry and multicolor immunophenotyping.
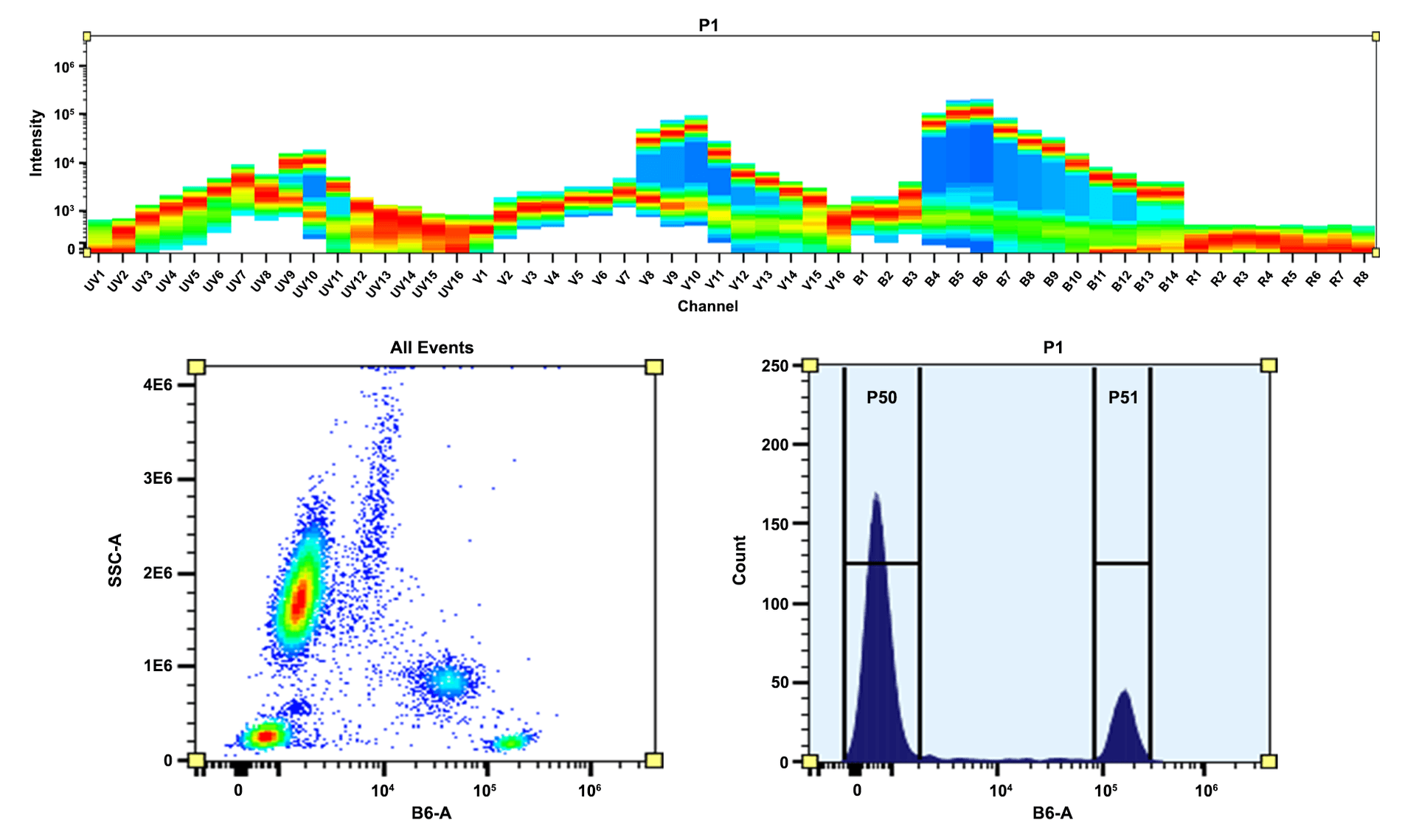
- High Brightness & Photostability: Delivers strong, stable fluorescence, enabling sensitive detection of low-abundance targets
- Optimized for Flow Cytometers: Efficient excitation with 488/561 nm lasers; compatible with 610/20 nm filters for streamlined multicolor panel design
- Enhanced Signal Resolution: Higher quantum yield and lower background than PE-Texas Red, improving signal-to-noise ratios and reducing spectral spillover

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2600 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | ~240000 |
| Solvent | Water |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 566 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 1960000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 565 |
| Emission (nm) | 606 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Refrigerated (2-8 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 13, 2026

