Signal Guard™ phosphatase reaction stopping solution
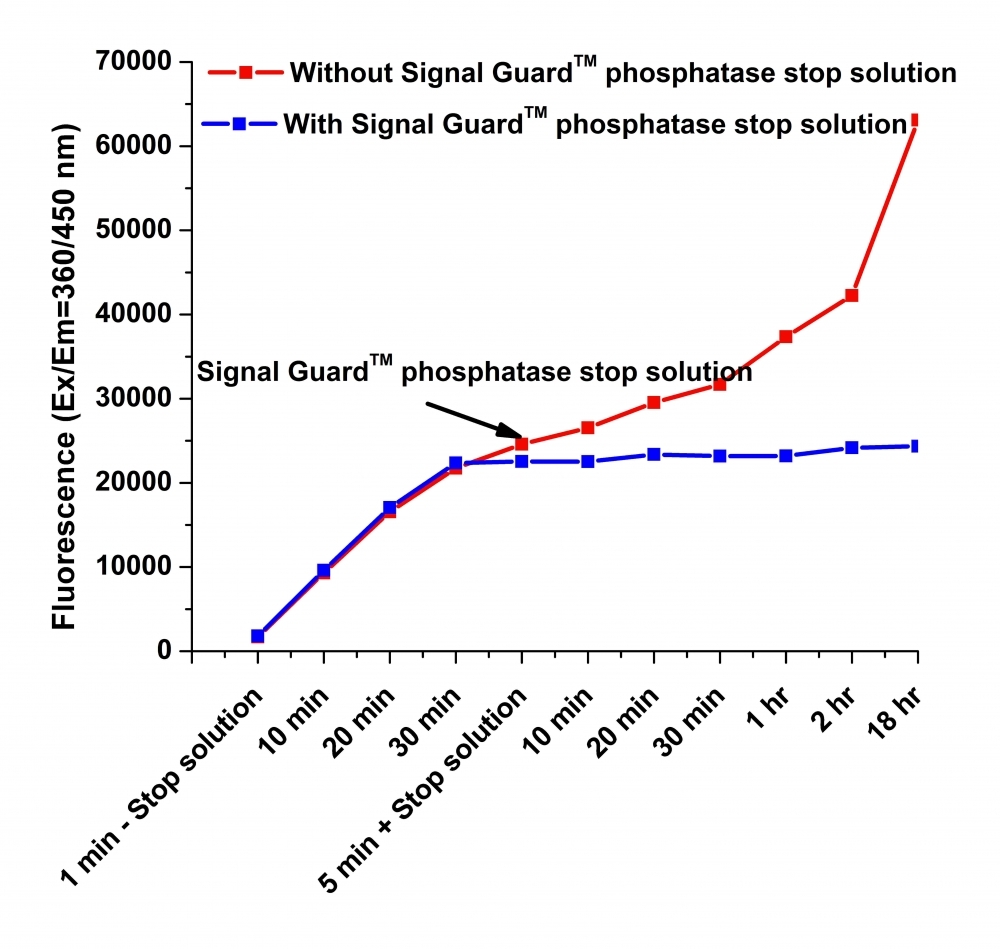
Alkaline and acid phosphatases are the hydrolase enzymes responsible for dephosphorylation of molecules such as nucleotides, proteins and alkaloids under alkaline and acidic conditions, respectively. Some phosphatases assays and tests require the phosphatase reactions to be stopped for further analysis using the stop solutions. Our Signal Guard™ phosphatase reaction stopping solution is a ready to use reagent that provides a convenient tool for terminating fluorescence and colorimetric signal-generating phosphatase reactions at a user-determined time point, and also keep the fluorescence or colorimetric signal stable for up to 18 hours. The Signal Guard™ phosphatase reaction stopping solution is optimized and compatible with alkaline, acid and protein phosphatase. Compared to other commercial phosphatase stopping reagents, our Signal Guard™ phosphatases reaction stopping solution is nearly neutral and mild. It is compatible with a vast majority of colorimetric and fluorimetric phosphatase substrates while the stop reagents from other vendors are not compatible with most of fluorescence-based phosphatase assays due to their extremely high pH.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11622 | 100 mL | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Refrigerated (2-8 °C) |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 11, 2026
