Transfectamine™ 7000 siRNA Transfection Reagent
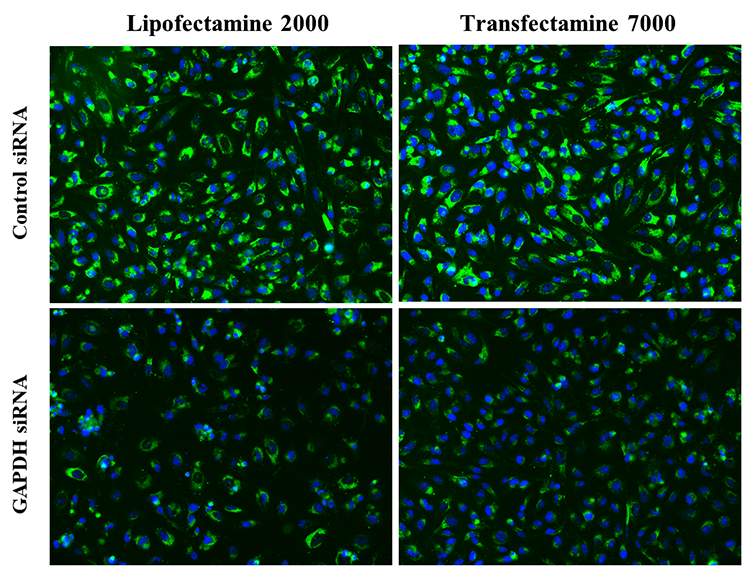
Transfectamine™ 7000 siRNA Transfection Reagent provides a reliable and effective solution for siRNA-mediated gene knockdown experiments, efficiently delivering small interfering RNA (siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) into diverse cell types. This reagent allows researchers to achieve high transfection efficiency with lower RNAi concentrations, resulting in effective gene knockdown with minimal non-specific effects. The low cytotoxicity of Transfectamine™ 7000 facilitates easy optimization across various concentration ranges, ensuring minimal impact on cell viability. The application protocol for Transfectamine™ 7000 is streamlined and rapid, promoting consistent and reproducible outcomes in gene silencing experiments. This reagent is capable of achieving significant levels of gene knockdown in a broad spectrum of cell lines, which is crucial for obtaining robust and conclusive experimental data. For high-throughput siRNA transfection applications, Transfectamine™ 7000 offers a straightforward workflow: the reagent is mixed with siRNA, applied to cells, incubated, and then the extent of gene knockdown is assessed. The efficiency and speed of this process, combined with the high transfection efficiency, makes Transfectamine™ 7000 an optimal choice for high-throughput screening, and it can be readily adapted for automated or robotic systems.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60025 | 1 mL | Price | |
| 60026 | 5 mL | Price | |
| 60027 | 50 uL | Price |
Physical properties
| Solvent | Water |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 11, 2026
