Z-IETD-ProRed™ 620
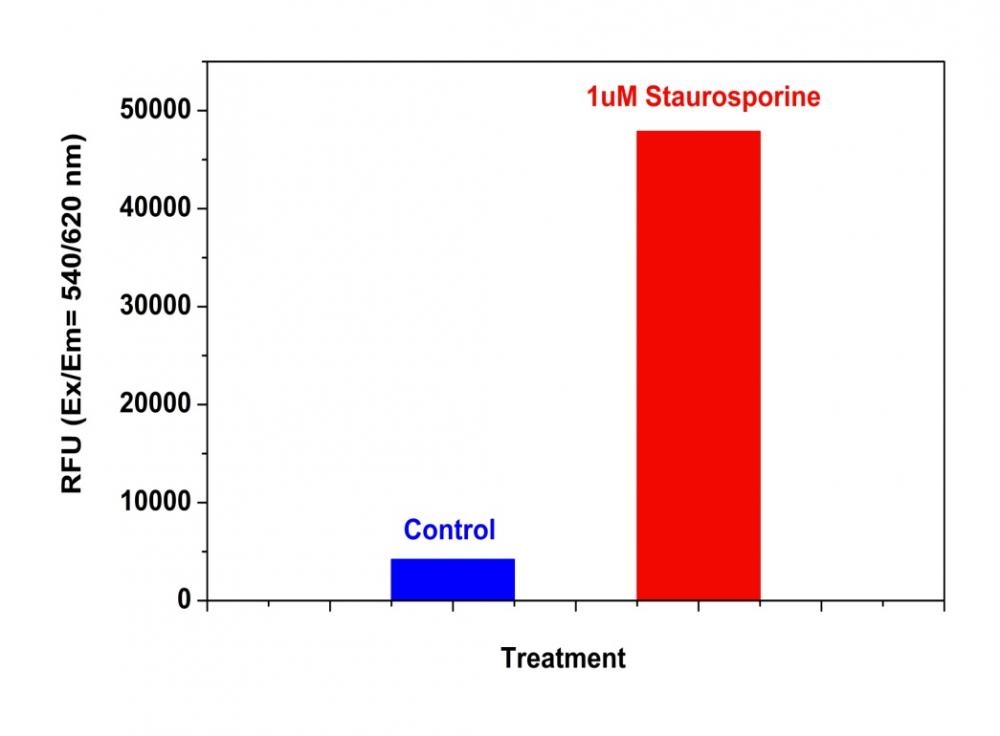
ProRed™-derived protease substrates are colorless and non-fluorescent. Cleavage of blocking protease-cleavable peptide residue by caspases generates the strongly red fluorescent ProRed™ that can be monitored fluorimetrically at ~620 nm with excitation of ~530 nm. ProRed™-derived caspase substrates are the most sensitive red indicators for the fluorimetric detection of various caspase activities. This IETD-ProRed™ substrate is specific for detecting caspase 8.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13434 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1565.59 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 532 |
| Emission (nm) | 619 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

