Amplite® Fluorimetric HDAC Activity Assay Kit
Green Fluorescence
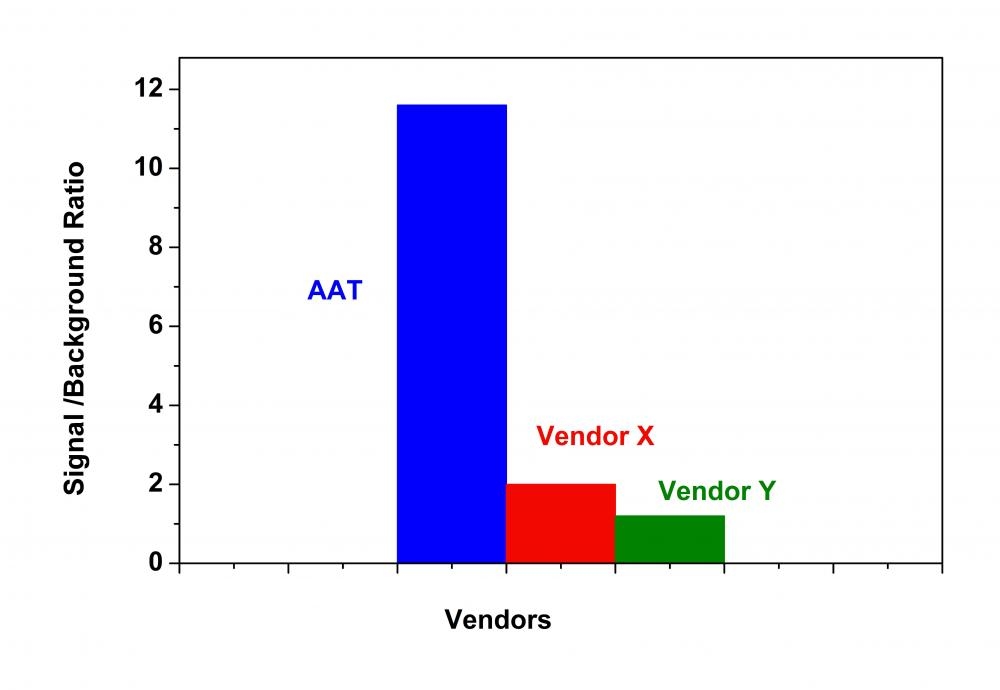
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from a ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone. Deacetylation restores the positive electric charge of the lysine amino acids, which increases the histone's affinity for the negatively charged phosphate backbone of DNA. This generally down-regulates DNA transcription by blocking the access of transcription factors. HDACs are involved in the pathway by which the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) suppresses cell proliferation. The pRb protein is part of a complex which attracts HDACs to the chromatin so that it will deacetylate histones. HDAC inhibitors are being studied as a treatment for cancer. The Amplite® HDAC Assay Kit provides a quick, convenient, and sensitive method for the detection of HDAC activity. Our HDAC Green™ substrate is much more resistant than other commercial peptide-based HDAC substrates. Our kit can be used for measuring HDAC activity in cell lysates, in vitro inhibitor screening with extracts or purified enzymes. The long wavelength emission and higher extinction coefficient of the HDAC Green™ substrate provide less interference from compounds and cell components. HDAC activity is determined by monitoring the green fluorescence enhancement with excitation at 490 nm and emission at 520 nm.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13601 | 200 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 493 |
| Emission (nm) | 520 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm |
| Emission | 525 nm |
| Cutoff | 515 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 10, 2026

