Amplite® Fluorimetric NADP/NADPH Ratio Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence
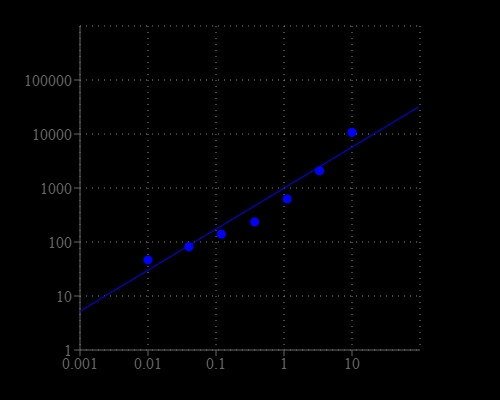
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) are two important cofactors found in cells. NADH is the reduced form of NAD+, and NAD+ is the oxidized form of NADH. It forms NADP with the addition of a phosphate group to the 2' position of the adenyl nucleotide through an ester linkage. NADP is used in anabolic biological reactions, such as fatty acid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent. The traditional NAD/NADH and NADP/NADPH assays are done by monitoring of NADH or NADPH absorption at 340 nm. This method suffers low sensitivity and high interference since the assay is done in the UV range that requires expensive quartz microplate. Our Amplite® NADP/NADPH Ratio Assay Kit provides a convenient method for sensitive detection of NADP, NADPH and their ratio. The enzymes in the system specifically recognize NAD/NADH in an enzyme cycling reaction. There is no need to purify NADP/NADPH from sample mix. The enzyme cycling reaction significantly increases detection sensitivity. In addition, this assay has very low background since it is run in the red visible range that significantly reduces the interference from biological samples. The assay has demonstrated high sensitivity and low interference. This Amplite® Fluorimetric NADP/NADPH Assay Kit can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microtiter-plate format and easily adapted to automation with no separation steps required.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15264 | 250 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Absorbance microplate reader | |
| Absorbance | 576 ± 5 nm |
| Recommended plate | Clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 540 nm |
| Emission | 590 nm |
| Cutoff | 570 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 4, 2026
