Amplite® Fluorimetric Sphingomyelin Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence
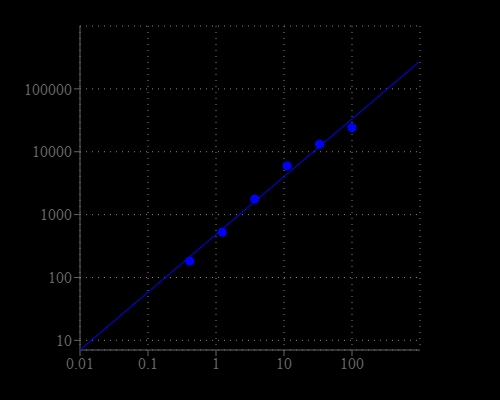
Sphingomyelin (SM) is largely found in the exoplasmic leaflet of the cell membrane, primarily in nervous tissue. It plays an important role in signal transduction. It accumulates abnormally in Niemann-Pick disease and Abetalipoproteinemia. Our Amplite® Fluorimetric Sphingomyelin Assay Kit provides the most sensitive method for detecting neutral SM activity or screening its inhibitors. The kit uses Amplite® Red as a fluorogenic probe to indirectly quantify the phosphocholine produced from the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin (SM) by sphingomyelinase (SMase). It can be used for measuring the SM in blood, cell extracts or other solutions. The fluorescence intensity of Amplite® Red is proportional to the formation of phosphocholine, therefore to the amount of SM. Amplite® Red enables the assay readable either in fluorescence intensity or absorption mode. The kit is an optimized "mix and read" assay that can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microtiter-plate format and easily adapted to automation without a separation step.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13625 | 100 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 571 |
| Emission (nm) | 584 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 540 nm |
| Emission | 590 nm |
| Cutoff | 570 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

