Cell Meter™ Live Cell Caspase 6 Binding Assay Kit
Green Fluorescence
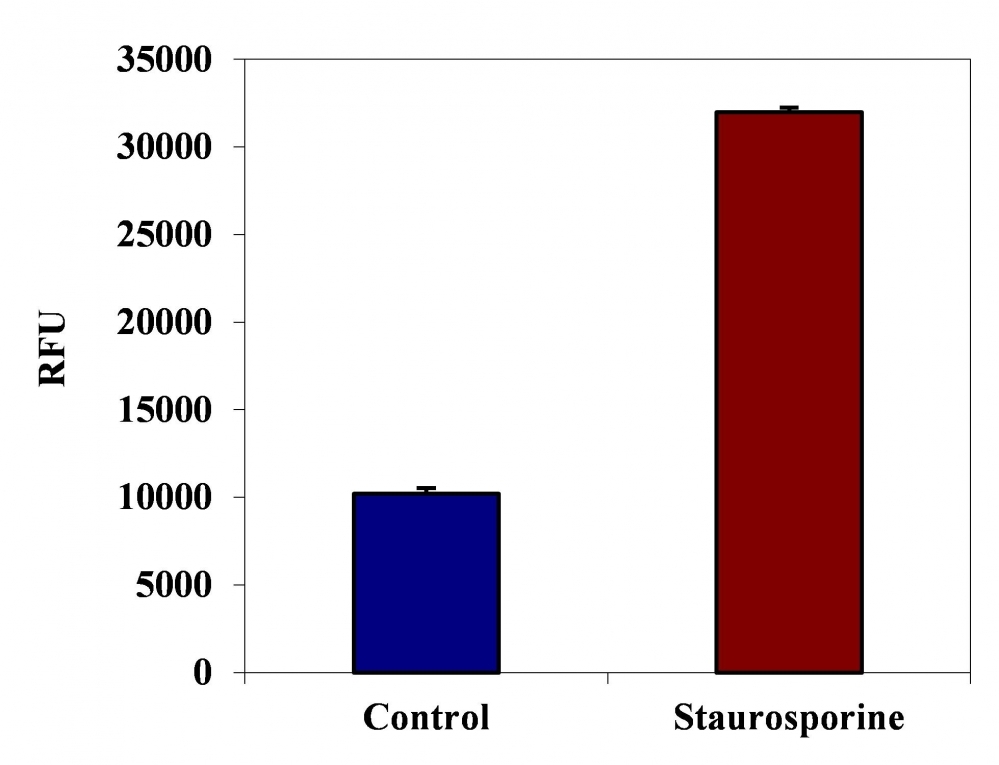
Our Cell Meter™ live cell caspases activity assay kits are based on fluorescent FMK inhibitors of caspases. These inhibitors are cell permeable and non-cytotoxic. Once inside the cell, the caspase inhibitors bind covalently to the active caspases. This Cell Meter™ Live Cell Caspase 6 Activity Assay Kit is designed to detect cell apoptosis by measuring caspase 6 activation in live cells. It is used for the quantification of activated caspase 6 activities in apoptotic cells, or for screening caspase 6 inhibitors. FAM-VEID-FMK, the green label reagent, allows for direct detection of activated caspase 6 in apoptotic cells by fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometer, or fluorescent microplate reader. The kit provides all the essential components with an optimized assay protocol.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20113 | 25 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.32 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.178 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 83000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 493 |
| Emission (nm) | 517 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | See Table 1 |
| Emission | See Table 1 |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | See Table 1 |
| Emission | See Table 1 |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | See Table 1 |
| Emission | See Table 1 |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

