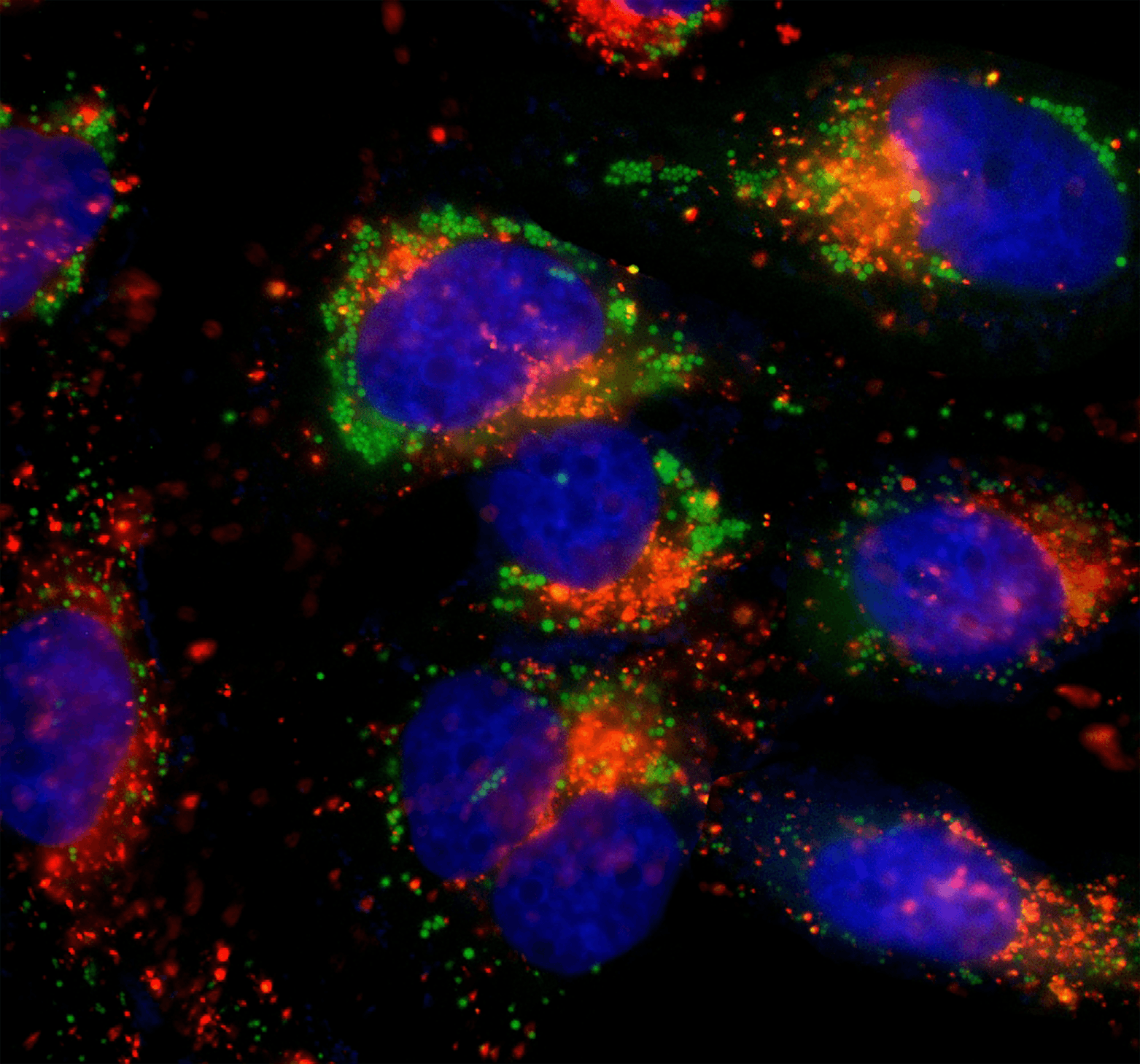
The Hoechst stains are a family of fluorescent stains for labeling DNA in fluorescence microscopy. Because these fluorescent stains label DNA, they are also commonly used to visualize nuclei and mitochondria. Two of these closely related bis-benzimides are commonly used: Hoechst 33258 and Hoechst 33342. Both dyes are excited by ultraviolet light at around 350 nm, and both emit blue/cyan fluorescence light around an emission maximum at 461 nm. The Hoechst stains may be used on live or fixed cells, and are often used as a substitute for another nucleic acid stain, DAPI. The key difference between them is that the additional ethyl group of Hoechst 33342 renders it more lipophilic, and thus more able to cross intact cell membranes. In some applications, Hoechst 33258 is significantly less permeant. These dyes can also be used to detect the contents of a sample DNA by plotting a standard emission-to-content curve.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17535 | 5 mL | Price |
| Molecular weight | 561.93 |
| Solvent | Water |
| Excitation (nm) | 352 |
| Emission (nm) | 454 |
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H340 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R68 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 41116134 |
| CAS | 875756-97-1 |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | 350 nm |
| Emission | 461 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |

