JC-10
Superior alternative to JC-1
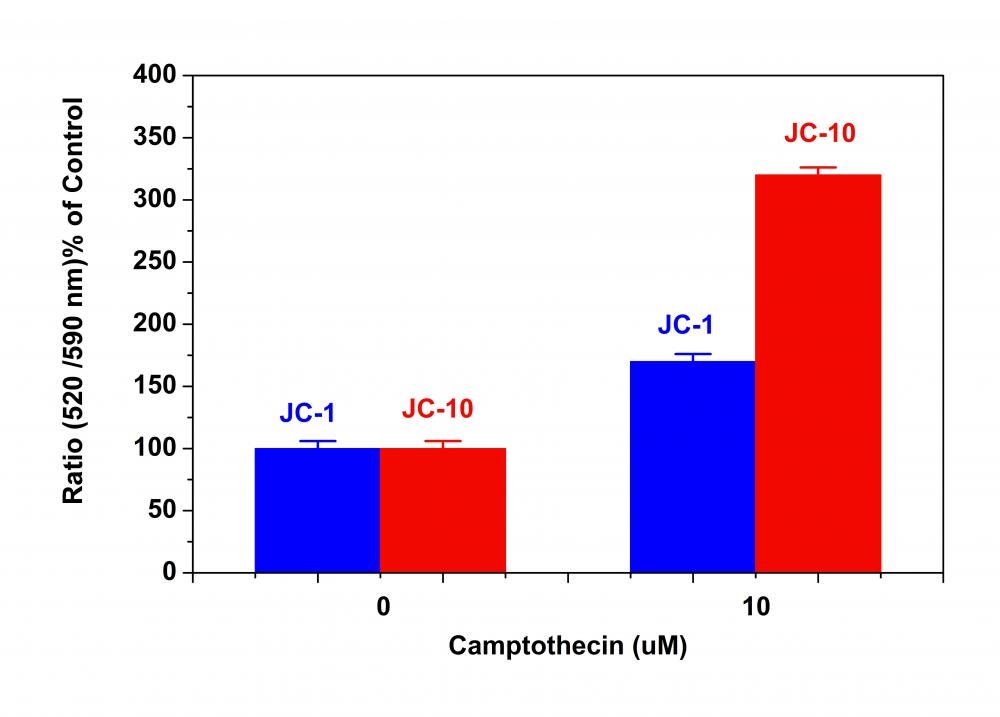
Although JC-1 is widely used in many labs, its poor water solubility makes it hard to use for some applications. Even at 1 µM concentration, JC-1 tends to precipitate in aqueous buffer. JC-10 has been developed to be an alternative to JC-1 where high dye concentration is desired. Compared to JC-1, our JC-10 has much better water solubility. JC-10 is capable of entering selectively into mitochondria, and changes reversibly its color from green to orange as membrane potentials increase. This property is due to the reversible formation of JC-10 aggregates upon membrane polarization that causes shifts in emitted light from 520 nm (i.e., emission of JC-10 monomeric form) to 570 nm (i.e., emission of J-aggregate). When excited at 490 nm, the color of JC-10 changes reversibly from green to greenish orange as the mitochondrial membrane becomes more polarized. Both colors can be detected using the filters commonly mounted in all flow cytometers, so that green emission can be analyzed in fluorescence channel 1 (FL1) and greenish orange emission in channel 2 (FL2). Besides its potential use in flow cytometry, it can also be used in fluorescence imaging. We have developed a protocol to use JC-10 in fluorescence microplate platform. In some cell lines JC-10 has even superior performance to JC-1. Interestingly the performance of JC-10 is quite cell line-dependent. Our JC-10 is conveniently provided in DMSO solution at ~3 mM concentration (2 mg/mL).

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22204 | 5x100 uL | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 583.34 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 508 |
| Emission (nm) | 524 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm, 575/26 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC and PE channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC and TRITC filter set |
| Emission | FITC and TRITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026

