mFluor™ Blue 620 SE
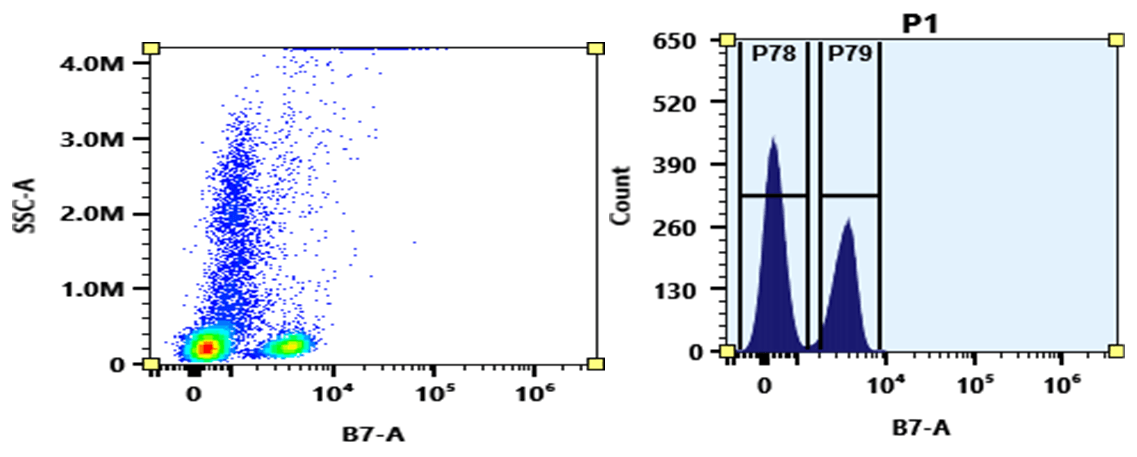
mFluor™ Blue 620 dye can be well excited with blue laser at 488 nm. It has a huge Stokes shift with emission ~620 nm. mFluor™ Blue 620 dyes are water-soluble, and the protein conjugates prepared with mFluor™ Blue 620 dyes are well excited at 488 nm to give red fluorescence. mFluor™ Blue 620 dye and conjugates are excellent blue laser reagents for flow cytometry detections. Compared to RPE, mFluor™ Blue 620 dyes are much more photostable, making them readily available for fluorescence imaging applications while it is very difficult to use RPE conjugates for fluorescence imaging applications due to the rapid photobleaching of RPE conjugates. It is also a unique fluorochrome for spectral flow cytometry since there are very few existing dyes that have this spectral profile.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1163 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1743.06 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 591 |
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.683 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.849 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 98000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 499 |
| Emission (nm) | 616 |
| Quantum yield | 0.18 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 31, 2026

