Cell Meter™ 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assay Kit
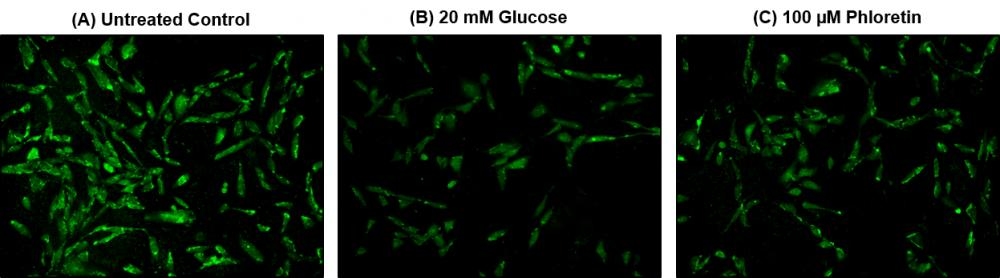
Glucose metabolism, a process which converts glucose into energy, is a primary source of energy supply in most organisms. 2-NBDG [2-(N-(7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino)-2-deoxyglucose], a fluorescently tagged glucose tracer, has been proven to effectively monitor glucose transportation in cells, as 2-NBDG transports into cells by the same glucose transporters (GLUTs) as glucose. Once 2-NBDG is uptaken in cells, it undergoes phosphorylation at C-6 position to give 2-NBDG-6-phosphate, which is well retained within the cells. Compared to other glucose tracers, such as 2-DG or FDG, 2-NBDG allows in situ measurements of 2-NBDG with high temporal and spatial resolution at single cell level. AAT Bioquest's Cell Meter™ 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assay Kit provides a sensitive and non-radioactive assay for measuring glucose uptake in cultured cells. In this kit, Assay Buffer I is used to enhance the uptake and retention of 2-NBDG in cells, while Assay Buffer II can improve the signal-to-background ratio of 2-NBDG in the cells. The fluorescence signal can be monitored by fluorescence microscope or flow cytometer with a 488 nm laser and 530/30 nm emission filter (FITC channel). Cell Meter™ 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assay Kit is the most robust tool for monitoring glucose transporters.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23500 | 200 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 467 |
| Emission (nm) | 538 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter |
| Emission | FITC filter |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 8, 2026

