iFluor® 488-Concanavalin A Conjugate
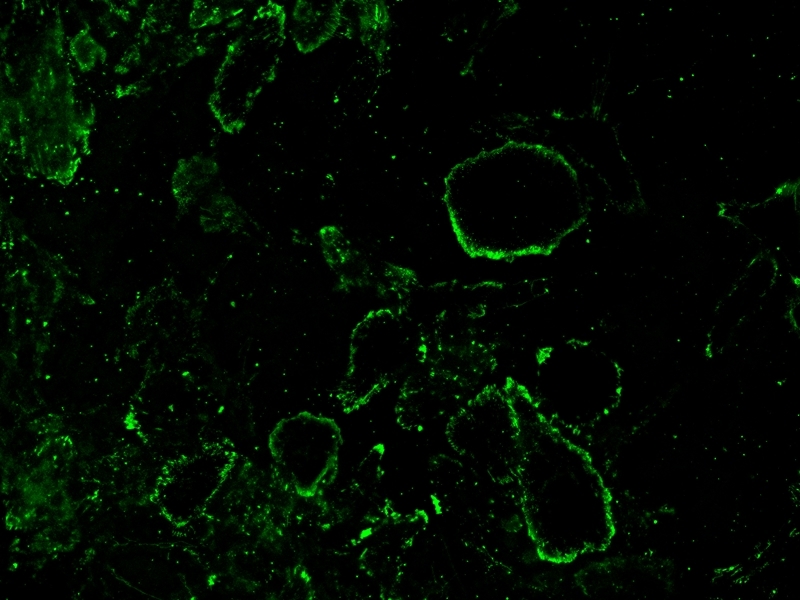
Concanavalin A (ConA) is a lectin that binds specifically to certain structures found in various sugars, glycoproteins and glycolipids. Con A is a well-known T cell mitogen that can activate the immune system, recruit lymphocytes and elicit cytokine production. In addition to its mitogenic activity, ConA can induce programmed cell death via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and autophagy. ConA has also been reported to activate NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells), a family of transcription factors that are important in the development and function of the immune system, including T cell receptor (TCR) engagement. ConA is widely used in biology and biochemistry to characterize glycoproteins and other sugar-containing entities on the surface of various cells. It is also used to purify glycosylated macromolecules in lectin affinity chromatography, as well as to study immune regulation by various immune cells. ConA binds specifically α-D-mannosyl and α-D-glucosyl residues (two hexoses differing only in the alcohol on carbon 2) in terminal position of ramified structures from B-Glycans. It has 4 binding sites, corresponding to the 4 subunits. Concanavalin A (Con A) is one of the most widely used lectins in cell biology. iFluor®488-labeled Concanavalin A selectively binds to a-mannopyranosyl and a-glucopyranosyl residues and might exhibit the brightest green fluorescence.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25580 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | N/A |
| Solvent | Water |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.21 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.11 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 75000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 491 |
| Emission (nm) | 516 |
| Quantum yield | 0.9 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter set |
| Emission | FITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 10, 2026

