MycoLight™ Bacterial Viability Assay Kit
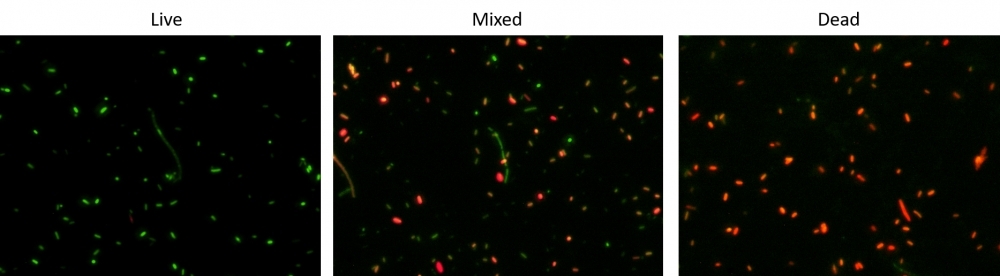
AAT Bioquest's Mycolight™ Bacterial Viability Assay Kit provides two-color fluorescence assay of bacterial viability in both gram-positive and negative bacterial cell. The kit utilizes the mixture of our green fluorescent nucleic acid stain MycoLight™ Green and the red-fluorescent nucleic acid stain propidium iodide. When used alone, the MycoLight™ Green stain generally labels all bacteria (live and dead) in a population. In contrast, propidium iodide penetrates only bacteria with damaged membranes, causing a reduction in the MycoLight™ Green stain fluorescence when both dyes are present. Thus, with an appropriate mixture of the MycoLight™ Green and propidium iodide stains, live bacteria with intact cell membranes emits green fluorescence, whereas dead or dying bacteria with damaged membranes gives red fluorescence. The Mycolight ™ Bacterial Viability Assay Kit is a robust tool for monitoring the viability of bacterial populations as a function of the membrane integrity of the cell. Stained cells can be monitored fluorimetrically at 510-530 nm (FITC filter) and 600-660 nm (Texas red filter) with excitation at 488 nm, the most common excitation light source.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22400 | 200 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 482 |
| Emission (nm) | 512 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H301, H311, H331 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R23, R24, R25 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm, 610/20 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC, PE-Texas Red channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | 510/600 nm |
| Emission | 530/660 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC/Texas Red filter sets |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 18, 2026

