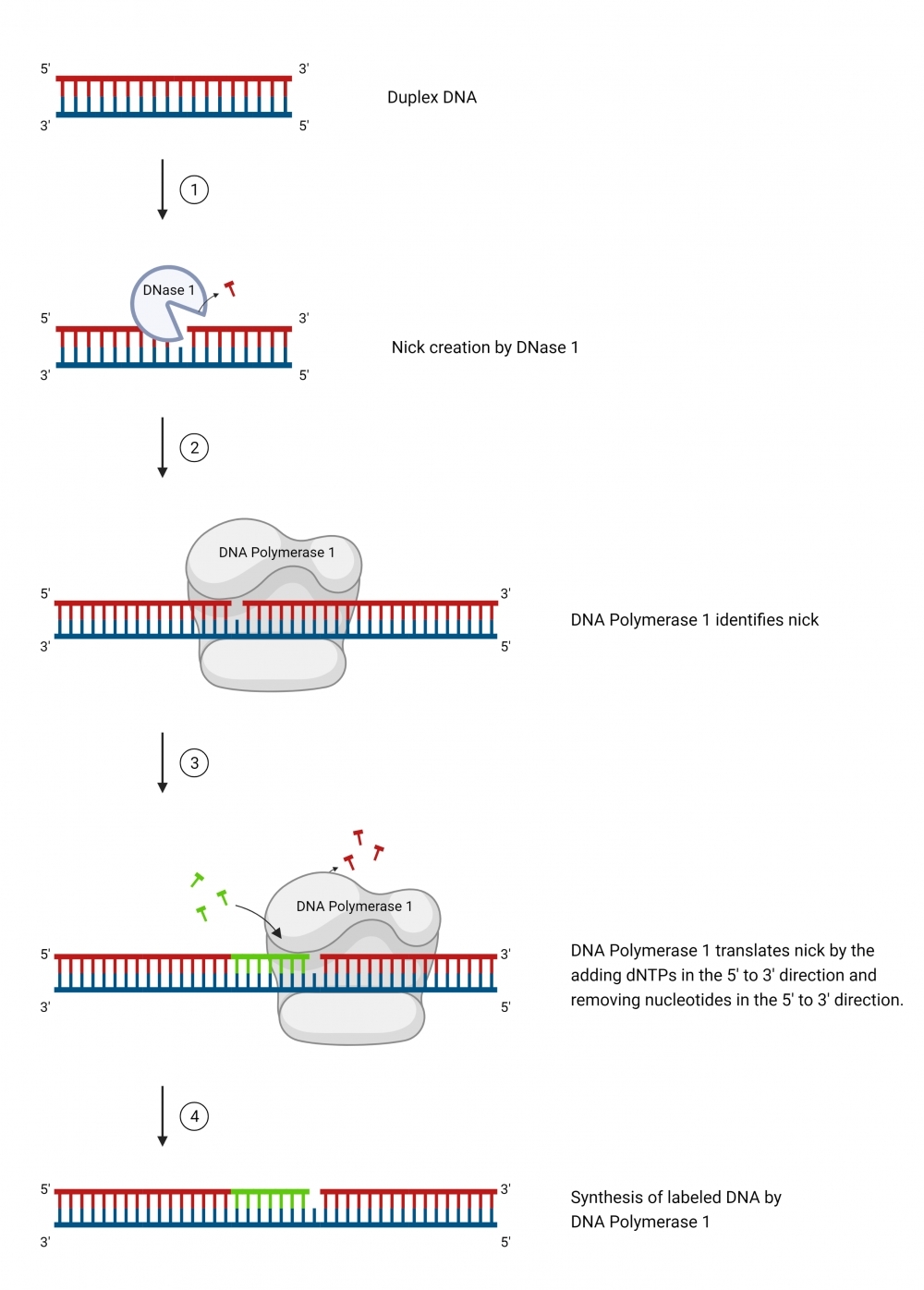
ReadiLink™ Biotin Nick Translation dsDNA Labelling Kit provides a simple and efficient way to label a double stranded DNA sample with Biotin tag. The labelling kit provides all necessary reagents for a complete workflow required for DNA labelling. This method utilizes a combination of DNAse and DNA polymerase to nick one strand of the DNA helix, to which Biotin is conjugated. In addition, the kit allows the user to optimize incorporation and product size by adjusting the ratio of Biotin-dUTP conjugate to dTTP. It is compatible with a wide variety of sample materials, including bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) DNA, human genomic DNA, purified PCR products, supercoiled and linearized plasmid DNA. The resulted Biotin-labeled DNAs can be used in a variety of molecular biology techniques such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17470 | 10 Reactions | Price | |
| 17471 | 20 Reactions | Price |
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
| Other instruments | Thermal Cycler |
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
