ReadiUse™ Cell Detaching Buffer
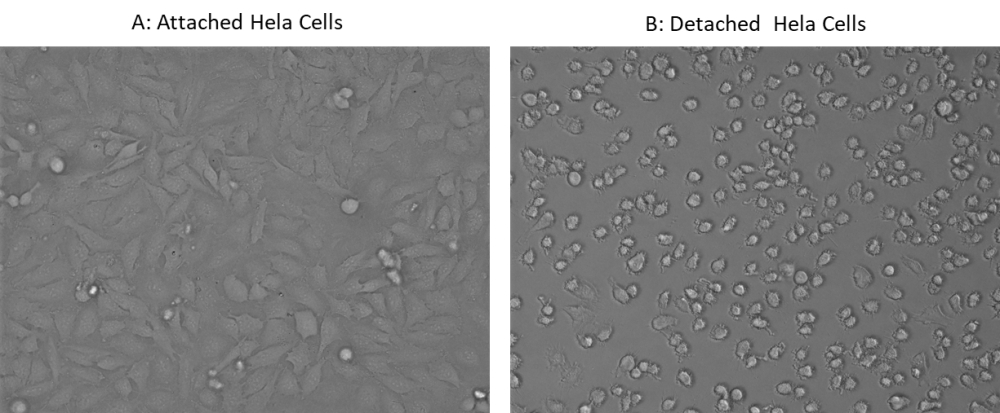
ReadiUse™ cell detaching buffer is a cell detachment solution that does not contain mammalian or bacterial-derived products. It works similar to trypsin with much less toxic effect. It performs exceptionally well in detaching primary and stem cells and maintains high cell viability. ReadiUse™ cell detaching buffer is very useful for routine cell passage, analysis of cell surface markers and receptors, cell proliferation, apoptosis and flow cytometry.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60010 | 50 mL | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 12, 2026
