StrandBrite™ Green Fluorimetric RNA Quantitation Kit
Optimized for Microplate Readers
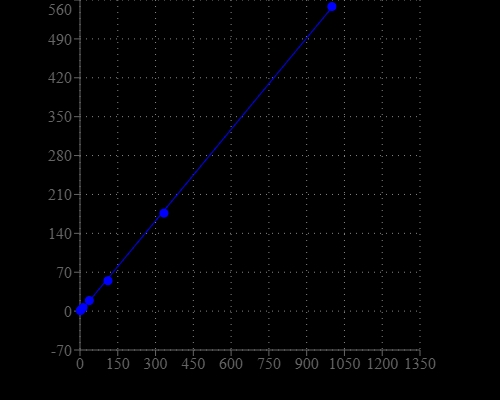
Detecting and quantitating small amounts of RNA is extremely important for a wide variety of molecular biology procedures such as measuring yields of in vitro transcribed RNA and measuring RNA concentrations before performing Northern blot analysis, S1 nuclease assays, RNase protection assays, cDNA library preparation, reverse transcription PCR, and differential display PCR. The most commonly used technique for measuring nucleic acid concentration is the determination of absorbance at 260 nm. The major disadvantage of the absorbance-based method is the interferences caused by proteins, free nucleotides and other UV absorbing compounds. The use of sensitive, fluorescent nucleic acid stains alleviates this interference problem. StrandBrite™ RNA quantifying reagent is an ultrasensitive fluorescent nucleic acid stain for quantitating RNA in solution. StrandBrite™ RNA quantifying reagent can detect as little as 5 ng/mL RNA with a fluorescence microplate reader or fluorometer. Our StrandBrite™ Green Fluorimetric RNA Quantitation Kit includes our StrandBrite™ Green nucleic acid stain with an optimized and robust protocol. It provides a convenient method for quantifying RNA in solutions.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17655 | 1000 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 509 |
| Emission (nm) | 527 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H340 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R68 |
| UNSPSC | 41116134 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm |
| Emission | 545 nm |
| Cutoff | 515 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 25, 2026

