Cell Navigator® Fluorimetric Lipid Droplet Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence
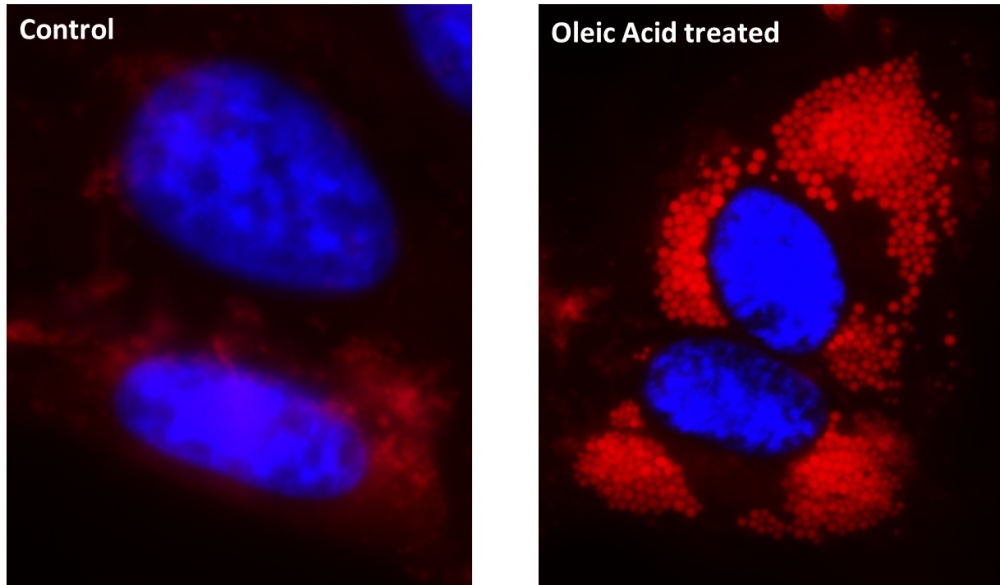
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids. They also serve as a reservoir of lipid source for many important biological processes such as fatty acid and cellular cholesterol for energy and membrane formation and maintenance. Abnormal accumulation of the cytoplasmic lipid droplets occurs in a variety of pathological conditions and can be an indicator of metabolic deficiency or pathogenesis. AAT Bioquest's Cell Navigator® Fluorimetric Lipid Droplet Assay Kit is a robust tool that could quantitatively measure lipid droplet accumulation. Droplite™ Red is used in the kit for lipophilic stain. Droplite™ Red is intensely fluorescent in a lipid-rich environment while it has minimal fluorescence in aqueous media. It is an excellent vital stain for the detection of intracellular lipid droplets with fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry or fluorescence microplate reader. The red fluorescence signal could be read observed using the filter set of TRITC.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22735 | 200 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 560 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 38000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 559 |
| Emission (nm) | 635 |
| Quantum yield | 0.7000 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | TRITC filter set |
| Emission | TRITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 550 nm |
| Emission | 640 nm |
| Cutoff | 610 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 30, 2026

