Calbryte™-520XL, AM is a new fluorescent and cell-permeable calcium indicator with extremely low affinity. Like other dye AM cell loading, Calbryte™-520XL AM ester is non-fluorescent, and once it gets inside the cell, it is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterase and gets activated. The activated indicator is a polar molecule that can no longer freely diffuse through the cell membrane, essentially trapped inside cells. Calbryte™-520XL has a low affinity for calcium ions with a Kd ~300 uM, similar to the well-known Rhod 5N, but it is much more stable. Calbryte™-520XL produces a bright fluorescence signal in the presence of calcium ions in high concentration. It has an excitation and emission wavelength identical to Fluo-4. Thus, the same Fluo-4 assay settings can be readily applied to Calbryte™-520XL-based calcium assays. Calbryte™-520XL is an excellent alternative to Rhod-5N. We also offer Calbryte™-520XL, potassium salt (#20645), Calbryte™-520XL-dextran (#20648), Calbryte™-520XL azide (#20643) that can be readily conjugated to a carrier through the well-known click chemistry.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20646 | 10x50 ug | Price |
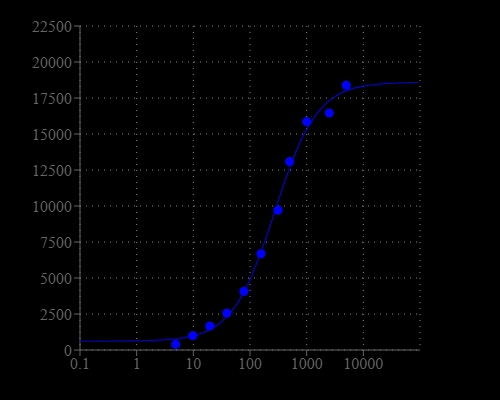
| Dissociation constant (Kd, nM) | 300000 |
| Molecular weight | 952.79 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
| Excitation (nm) | 493 |
| Emission (nm) | 515 |
| Quantum yield | 0.75 1 |
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC |
| Emission | FITC |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 |
| Emission | 525 |
| Cutoff | 515 |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode/Programmable liquid handling |
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |

