Cell Navigator® NBD Ceramide Golgi Staining Kit
Green Fluorescence
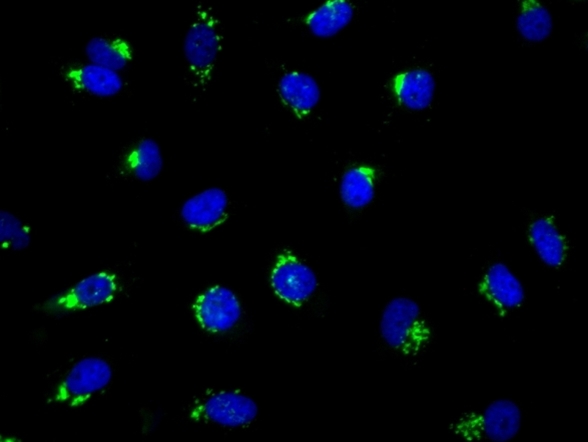
The Golgi apparatus is a complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport. It modifies proteins and lipids that have been built in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and prepares them for export outside of the cell. It also plays a significant role in the transport of lipids throughout the cell and the formation of lysosomes. This Cell Navigator® NBD Ceramide Golgi Staining kit provides a simple and rapid way to stain Golgi in live cells, or aldehyde-fixed cells selectively. C6 NBD Ceramide is administered to cells as a complex with bovine serum albumin (C6-NBD-Ceramide-BSA). Golgi apparatus is stained through the formation of the respective fluorescent metabolites. This Cell Navigator® NBD Ceramide Golgi Staining Kit provides an optimized assay method for examining the morphology of the Golgi apparatus with a fluorescence microscope.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22750 | 100 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 467 |
| Emission (nm) | 538 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | 488 nm |
| Emission | 525 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC filterset |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 10, 2026

