PhosphoWorks™ Luminometric ATP Assay Kit
Extended Luminescence
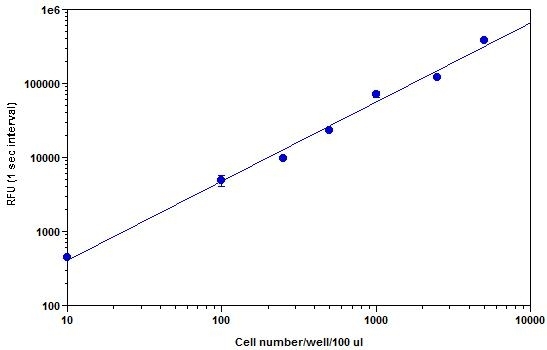
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a fundamental role in cellular energenics, metabolic regulation and cellular signaling. The PhosphoWorks™ ATP Assay Kit provides a fast, simple and homogeneous luminescence assay for the determination of cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in mammalian cells. The assay can be performed in a convenient 96-well and 384-well microtiter-plate format. The high sensitivity of this assay permits the detection of ATP in many biological systems, environmental samples and foods. This PhosphoWorks ATP Assay Kit has the stable luminescence signal as long as 4 hours. It has stable luminescence with no mixing or separations required, and formulated to have minimal hands-on time.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21608 | 10 Plates | Price | |
| 21609 | 1 Plate | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Luminescence microplate reader | |
| Recommended plate | Solid white |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 23, 2026
