iFluor® 594 amine
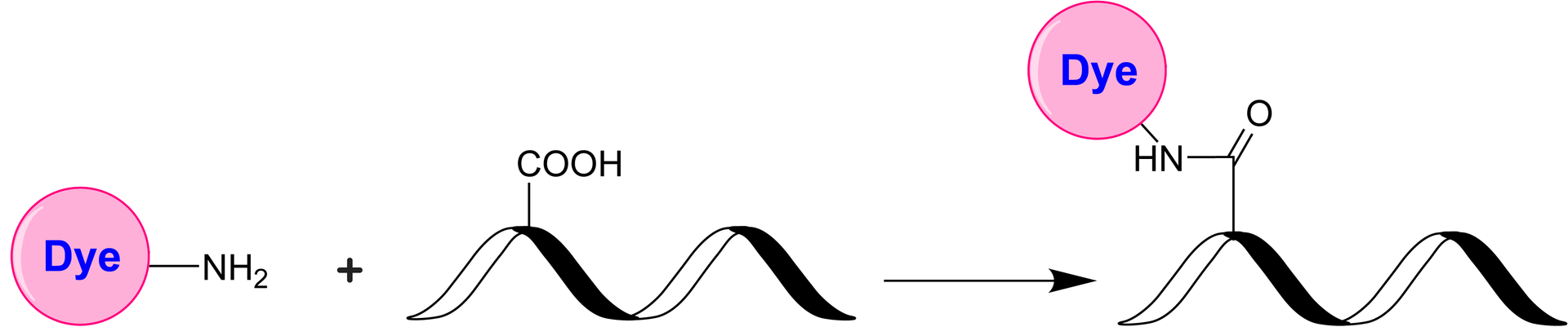
iFluor® 594 amine is a red-fluorescent dye with a reactive primary amine that enables conjugation to activated carboxyl groups via EDC chemistry, ideal for labeling proteins, peptides, and oligonucleotides.
- Versatile Conjugation: Efficiently labels carboxyl groups and also serves as an amine donor for enzymatic transamination labeling
- High Photostability & Brightness: Delivers strong fluorescence signals with minimal photobleaching, ideal for imaging and flow cytometry applications
- Broad pH Stability: Maintains consistent fluorescence across a wide pH range (pH 3–11), enabling use in diverse biological environments

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1089 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1017.08 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 587 |
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.05 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.04 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 200000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 587 |
| Emission (nm) | 603 |
| Quantum yield | 0.53 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 2, 2026

