mFluor™ Violet 500-Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) Conjugate
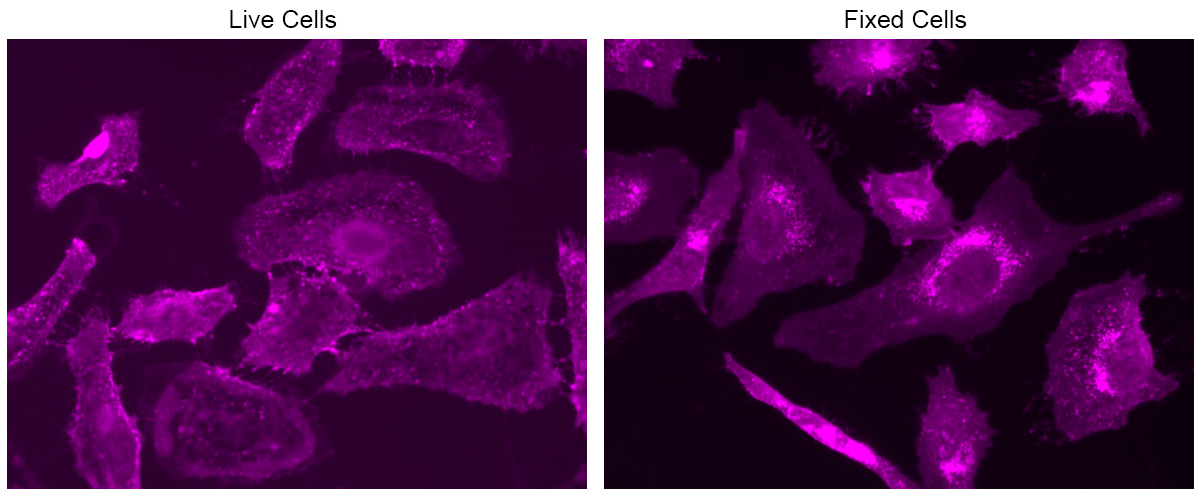
Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) is a well-studied lectin known for its binding affinity to N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and sialic acid, making it a valuable tool in various biological applications. Its interaction with glycoconjugates enables widespread use of WGA derivatives and conjugates for fluorescence imaging and analysis, facilitating the labeling of yeast bud scars, fibrotic scar tissue, and the cell membranes of gram bacteria and mammalian cells. WGA specifically targets sequences of β-1,4-GlcNAc-linked residues known as chitodextrins. Each monomer contains two identical, non-interacting binding sites complementary to 3 or 4 β-1,4-GlcNAc units. Among the monosaccharides tested, only GlcNAc shows strong binding to WGA, while ManNAc demonstrates no binding, and GalNAc exhibits weak binding. The mFluor™ Violet 500 labeled WGA is well-excited by the violet laser, emitting a bright green fluorescence at 501 nm. Notably, the mFluor™ Violet 500 WGA conjugate retains its ability to bind to sialic acid and N-acetylglucosaminyl residues, enhancing its utility in fluorescence imaging and analysis of various scientific investigations.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25452 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Solvent | Water |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 412 |
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.769 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.365 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 25000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 410 |
| Emission (nm) | 501 |
| Quantum yield | 0.81 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | 410 nm |
| Emission | 501 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on October 8, 2024

