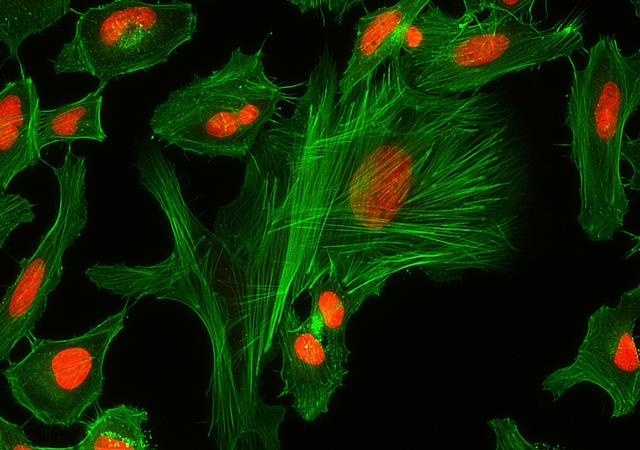
Phalloidin Conjugates
XFD488 Same Structure to Alexa Fluor™ 488
XFD488 is manufactured by AAT Bioquest, and it has the same chemical structure of Alexa Fluor® 488 (Alexa Fluor® is the trademark of ThermoFisher). XFD488 phalloidin conjugate is chemically equivalent to Alexa Fluor® 488 phalloidin. This green fluorescent phalloidin conjugate selectively binds to F-actins. Used at nanomolar concentrations, phalloidin derivatives are convenient probes for labeling, identifying and quantitating F-actins in formaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized tissue sections, cell cultures or cell-free experiments. Fluorescent phalloidin derivatives have been used as an important tool in the study of actin networks at high resolution. AAT Bioquest offers a variety of fluorescent phalloidin derivatives with different colors for multicolor imaging applications.
Example protocol
AT A GLANCE
Protocol Summary
- Prepare samples in microplate wells
- Remove liquid from samples in the plate
- Add XFD488 Phalloidin Conjugate solution (100 μL/well)
- Stain the cells at room temperature for 20 to 90 minutes
- Wash the cells
- Examine the specimen under microscope with FITC filter
Storage and Handling Conditions
The solution should be stable for at least 6 months if store at -20 °C. Protect the fluorescent conjugates from light, and avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Note: Phalloidin is toxic, although the amount of toxin present in a vial could be lethal only to a mosquito (LD50 of phalloidin = 2 mg/kg), it should be handled with care.PREPARATION OF WORKING SOLUTION
XFD488 Phalloidin Conjugate working solution
Add 1 µL of XFD488 Phalloidin Conjugate solution to 1 mL of PBS with 1% BSA. Note: The stock solution of phalloidin conjugate should be aliquoted and stored at -20 °C. protected from light. Note: Different cell types might be stained differently. The concentration of phalloidin conjugate working solution should be prepared accordingly.SAMPLE EXPERIMENTAL PROTOCOL
Stain the cells
- Perform formaldehyde fixation. Incubate cells with 3.0–4.0 % formaldehyde in PBS at room temperature for 10–30 minutes. Note: Avoid any methanol containing fixatives since methanol can disrupt actin during the fixation process. The preferred fixative is methanol-free formaldehyde.
- Rinse the fixed cells 2–3 times in PBS.
- Optional: Add 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS into fixed cells for 3 to 5 minutes to increase permeability. Rinse the cells 2–3 times in PBS.
- Add 100 μL/well (96-well plate) of XFD488 Phalloidin Conjugate working solution into the fixed cells, and stain the cells at room temperature for 20 to 90 minutes.
- Rinse cells gently with PBS 2 to 3 times to remove excess phalloidin conjugate before plating, sealing and imaging under microscope with FITC filter set.
Spectrum
Alternative formats
| Name | Conjugate |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 488 Conjugate | iFluor 488 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 647 Conjugate | iFluor 647 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 594 Conjugate | iFluor 594 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 555 Conjugate | iFluor 555 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 633 Conjugate | iFluor 633 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 532 Conjugate | iFluor 532 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 405 Conjugate | iFluor 405 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 514 Conjugate | iFluor 514 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 350 Conjugate | iFluor 350 |
Show More (15) | |
Product family
| Name | Excitation (nm) | Emission (nm) | Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | Quantum yield | Correction Factor (260 nm) | Correction Factor (280 nm) |
| XFD350 Phalloidin *XFD350 Same Structure to Alexa Fluor™ 350* | 343 | 441 | 19000 | - | 0.25 | 0.19 |
| XFD555 Phalloidin *equivalent to Alexa Fluor® 555 phalloidin* | 553 | 568 | 150000 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| XFD594 Phalloidin *XFD594 Same Structure to Alexa Fluor™ 594* | 590 | 618 | 92000 | 0.661 | 0.43 | 0.56 |
| XFD647 Phalloidin *equivalent to Alexa Fluor® 647 phalloidin* | 650 | 671 | 239000 | 0.331 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| XFD750 Phalloidin *equivalent to Alexa Fluor® 750 phalloidin* | 752 | 776 | 240000 | 0.121 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
Citations
View all 31 citations: Citation Explorer
Atractylodin inhibits fructose-induced human podocyte hypermotility via anti-oxidant to down-regulate TRPC6/p-CaMK4 signaling
Authors: Chen, Li and Tang, Ya-Li and Liu, Zhi-Hong and Pan, Ying and Jiao, Rui-Qing and Kong, Ling-Dong
Journal: European journal of pharmacology (2021): 174616
Authors: Chen, Li and Tang, Ya-Li and Liu, Zhi-Hong and Pan, Ying and Jiao, Rui-Qing and Kong, Ling-Dong
Journal: European journal of pharmacology (2021): 174616
Dicalcin suppresses in vitro trophoblast attachment in human cell lines
Authors: Saito, Ryohei and Satoh, Hiromasa and Aoba, Kayo and Hirasawa, Hajime and Miwa, Naofumi
Journal: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2021): 206--213
Authors: Saito, Ryohei and Satoh, Hiromasa and Aoba, Kayo and Hirasawa, Hajime and Miwa, Naofumi
Journal: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2021): 206--213
Targeted Gene Disruption in Pacific Oyster Based on CRISPR/Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Complexes
Authors: Yu, Hong and Li, Huijuan and Li, Qi and Xu, Rui and Yue, Chenyang and Du, Shaojun
Journal: Marine Biotechnology (2019): 1--9
Authors: Yu, Hong and Li, Huijuan and Li, Qi and Xu, Rui and Yue, Chenyang and Du, Shaojun
Journal: Marine Biotechnology (2019): 1--9
Enhancing the cell-biological performances of hydroxyapatite bioceramic by constructing silicate-containing grain boundary phases via sol infiltration
Authors: Xu, Yubin and Lu, Teliang and He, Fupo and Ma, Ning and Ye, Ji and ong , undefined and Wu, Tingting
Journal: ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering (2018)
Authors: Xu, Yubin and Lu, Teliang and He, Fupo and Ma, Ning and Ye, Ji and ong , undefined and Wu, Tingting
Journal: ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering (2018)
Enhanced Osteogenesis of Injectable Calcium Phosphate Bone Cement Mediated by Loading Chondroitin Sulfate
Authors: Shi, Haishan and Ye, Xiaoling and Zhang, Jing and Ye, Ji and ong, undefined
Journal: ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering (2018)
Authors: Shi, Haishan and Ye, Xiaoling and Zhang, Jing and Ye, Ji and ong, undefined
Journal: ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering (2018)
References
View all 127 references: Citation Explorer
Improved penile histology by phalloidin stain: circular and longitudinal cavernous smooth muscles, dual-endothelium arteries, and erectile dysfunction-associated changes
Authors: Lin G, Qiu X, F and el TM, Albersen M, Wang Z, Lue TF, Lin CS.
Journal: Urology (2011): 970 e1
Authors: Lin G, Qiu X, F and el TM, Albersen M, Wang Z, Lue TF, Lin CS.
Journal: Urology (2011): 970 e1
Phalloidin perturbs the interaction of human non-muscle myosin isoforms 2A and 2C1 with F-actin
Authors: Diensthuber RP, Muller M, Heissler SM, Taft MH, Chizhov I, Manstein DJ.
Journal: FEBS Lett (2011): 767
Authors: Diensthuber RP, Muller M, Heissler SM, Taft MH, Chizhov I, Manstein DJ.
Journal: FEBS Lett (2011): 767
pH-(low)-insertion-peptide (pHLIP) translocation of membrane impermeable phalloidin toxin inhibits cancer cell proliferation
Authors: An M, Wijesinghe D, Andreev OA, Reshetnyak YK, Engelman DM.
Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010): 20246
Authors: An M, Wijesinghe D, Andreev OA, Reshetnyak YK, Engelman DM.
Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010): 20246
Labeling cytoskeletal F-actin with rhodamine phalloidin or fluorescein phalloidin for imaging
Authors: Chazotte B., undefined
Journal: Cold Spring Harb Protoc (2010): pdb prot4947
Authors: Chazotte B., undefined
Journal: Cold Spring Harb Protoc (2010): pdb prot4947
Pygmy squids and giant brains: mapping the complex cephalopod CNS by phalloidin staining of vibratome sections and whole-mount preparations
Authors: Wollesen T, Loesel R, Wanninger A.
Journal: J Neurosci Methods (2009): 63
Authors: Wollesen T, Loesel R, Wanninger A.
Journal: J Neurosci Methods (2009): 63
Page updated on October 9, 2024