iFluor® 647 succinimidyl ester
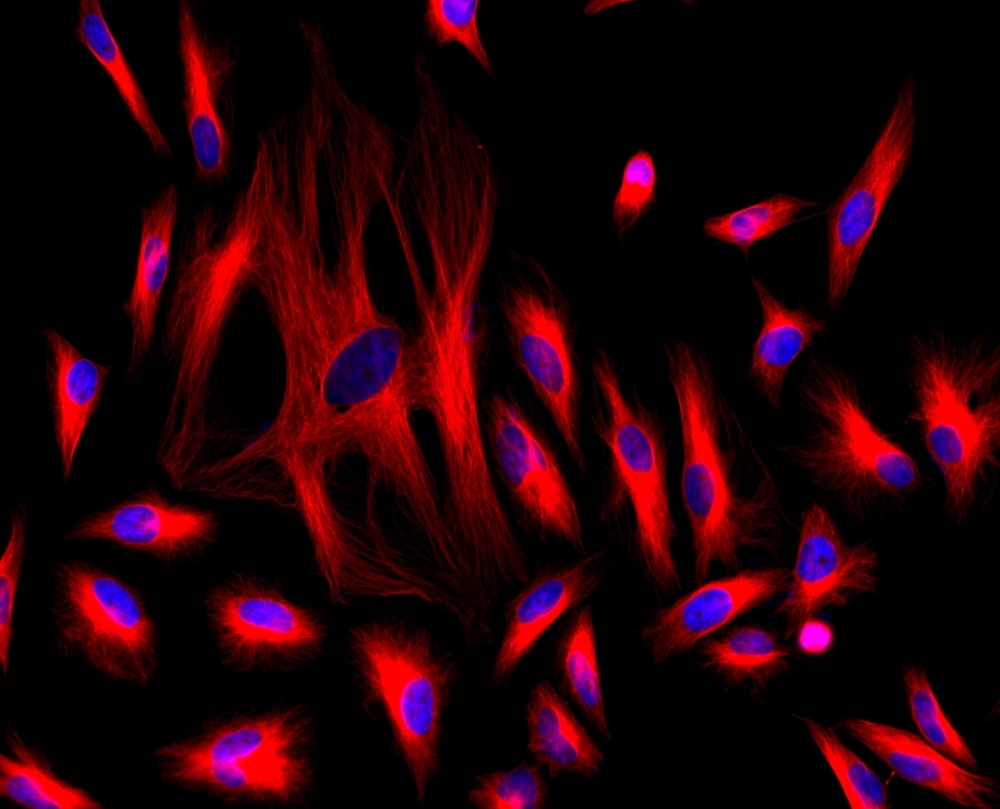
AAT Bioquest's iFluor® dyes are optimized for labeling proteins, particularly antibodies. These dyes are bright, photostable, and have minimal quenching on proteins. They can be well excited by the major laser lines of fluorescence instruments (e.g., 350, 405, 488, 555, and 633 nm). The iFluor® 647 family has spectral properties essentially identical to those of Cy5®. Compared to Cy5® probes, iFluor® 647 reagents have much stronger fluorescence and higher photostability. Their fluorescence is pH-independent from pH 3 to 11. These spectral characteristics make this new dye family an excellent alternative to Cy5® and Alexa Fluor® 647 (Cy5® and Alexa Fluor® are the trademarks of GE Health Care and Invitrogen). iFluor® 647 SE is reasonably stable and shows good reactivity and selectivity with protein amino groups.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1031 | 1 mg | Price | |
| 71031 | 100 ug | Price | |
| 71510 | 5 mg | Price | |
| 71560 | 10 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1274.66 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.03 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.03 |
| Correction factor (656 nm) | 0.0793 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 250000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 656 |
| Emission (nm) | 670 |
| Quantum yield | 0.25 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 6, 2026

