Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a core technique used extensively in molecular biology research to amplify a specific DNA template in vitro rapidly. It enables researchers to generate significant quantities of sample DNA for a wide range of downstream laboratory and clinical applications, including cloning, genotyping, sequencing, mutagenesis, forensics, and the detection of pathogens to diagnose infectious diseases. Since being introduced in 1985, several iterations of the PCR process have been developed, including quantitative PCR (qPCR) for monitoring DNA amplification in real-time and reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) for the detection of RNA, a tool that has become instrumental in viral diagnostics.
For accurate and sensitive PCR detection, AAT Bioquest offers a comprehensive portfolio of PCR reference dyes, deoxynucleotide triphosphates, double-stranded DNA-binding dyes, and fluorescent reporter dyes and non-fluorescent quenchers for the development of sequence-specific molecular beacons.
For accurate and sensitive PCR detection, AAT Bioquest offers a comprehensive portfolio of PCR reference dyes, deoxynucleotide triphosphates, double-stranded DNA-binding dyes, and fluorescent reporter dyes and non-fluorescent quenchers for the development of sequence-specific molecular beacons.
Principles of PCR
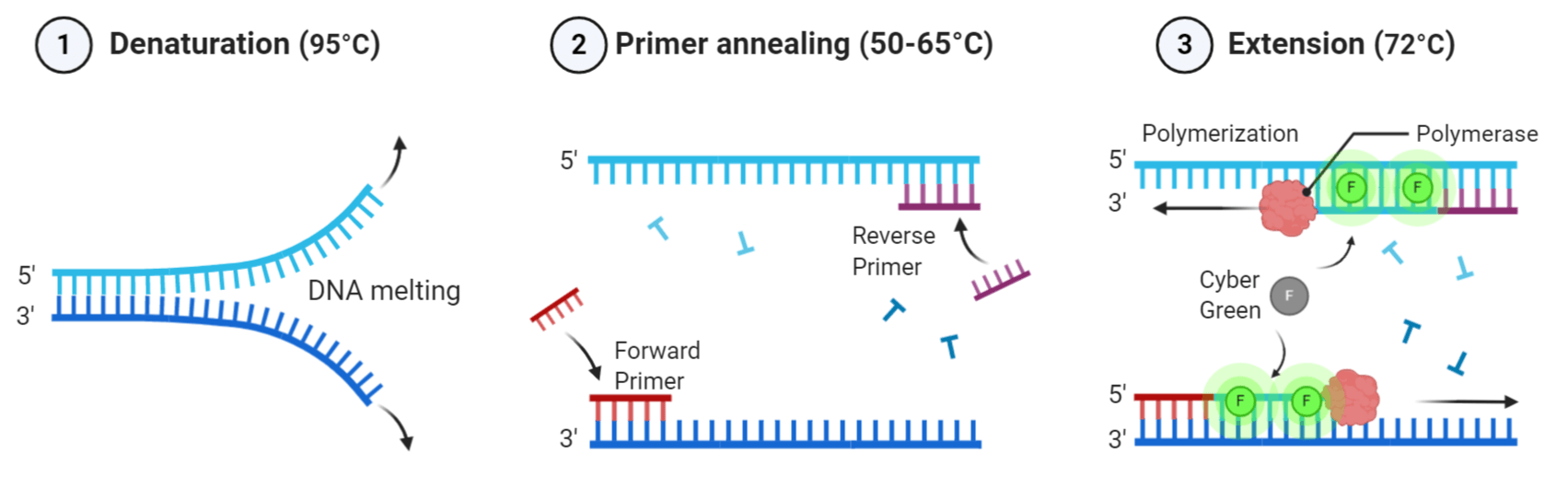
PCR is commonly used to amplify a single DNA template into millions or billions of identical copies in vitro. A typical amplification reaction requires a DNA template, thermostable DNA polymerase, forward and reverse primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and a reaction buffer (Table 1). The components are combined in a PCR or Eppendorf tube and then placed in a thermal cycler to facilitate the amplification process. While inside the thermal cycler, the PCR mixture undergoes a series of temperature and time adjustments which includes three key steps: (1) template denaturation, (2) primer annealing, and (3) primer extension.
PCR Process
During the denaturation process, the double-stranded DNA template is heated at 95°C for two minutes. The high temperature causes hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs in the DNA template to separate into two single-stranded components. Next, the temperature is reduced to 50-65°C for approximately 20-40 seconds to facilitate primer annealing to each single-stranded DNA. After annealing, the temperature is increased to 70-74°C to initiate elongation. In this step, DNA polymerases will bind to and extend the primer to form a nascent DNA strand. It does so by moving along the DNA template base by base in the 5' to 3' direction and adds the corresponding complementary dNTP from the reaction mixture. Altogether, these three steps are referred to as a PCR cycle, and after each cycle, the number of double-stranded DNA fragments doubles. PCR cycles are repeated 25 to 30 times to amplify the original DNA template exponentially.
Video 1. PCR animation. Animated video tutorial illustrating the three key steps in the polymerase chain reaction: (1) template denaturation, (2) primer annealing, and (3) primer extension.
Table 1. Summary of the components required for PCR
| PCR Component ▲ ▼ | Function ▲ ▼ |
| DNA Template | This is the sample DNA that contains the target sequence to be amplified. |
| Thermostable DNA polymerase | The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of new DNA strands complementary to the target sequence. Commonly used polymerases include TaqDNA polymerase and PfuDNA polymerase. |
| Primers (forward and reverse) | Short, single-stranded DNA sequences that hybridize to the sample DNA and start the process of replication. Primers are designed to complement the sequences at the beginning and end of the DNA template intended for amplifying. |
| Deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) | These are the "building blocks" from which the DNA fragments will be synthesized and are commonly available in a ready-to-use format, such as ReadiUse™ dNTP Mix *10 mM* (Cat No. 17200) |
| Reaction buffer containing magnesium | This provides a stable environment for the PCR reaction. It has a suitable pH of 8.0 to 9.5 and is fortified with magnesium chloride, a co-factor of DNA polymerase. |
Conventional Analysis of PCR Products
Once the PCR process is complete, the reaction products are stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr) and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the size and concentration of the DNA molecules. While ethidium bromide is the most commonly used dye for visualizing DNA, it is mutagenic and highly toxic through inhalation. Therefore, consider using non-toxic alternatives such as Helixyte™ Green (Cat No. 17590), Helixyte™ Gold (Cat No. 17595), Gelite™ Green (Cat No. 17589), or Gelite™ Orange (Cat No. 17594).
Table 2. Non-toxic DNA stains for agarose gel electrophoresis
| Product ▲ ▼ | Ex (nm) ▲ ▼ | Em (nm) ▲ ▼ | Unit Size ▲ ▼ | Cat No. ▲ ▼ |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X Water Solution* | 513 nm | 552 nm | 1 mL | 17702 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 513 nm | 552 nm | 1 mL | 17706 |
| Gelite™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit | 254 or 300 nm1 | Long path green filter2 | 1 Kit | 17589 |
| Gelite™ Orange Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit | 254 or 300 nm1 | Long path green filter2 | 1 Kit | 17594 |
| Helixyte™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 497 nm | 521 nm | 1 mL | 17590 |
| Helixyte™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 497 nm | 521 nm | 100 µL | 17604 |
| Helixyte™ Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 496 nm | 539 nm | 1 mL | 17595 |
- Excitation settings are for a transilluminator or laser-based gel scanner.
- Common long path green filters include the SYBR® filter and GelStar® filter.
Types of PCR
Conventional PCR methods, like the process aforementioned, can only amplify DNA and requires agarose gel electrophoresis to determine PCR success from the end-point of the reaction. This process is very time-consuming and is hindered by various caveats, including low sensitivity, low resolution, poor precision, non-automation, post-PCR processing, and a short dynamic range. To address these concerns, several iterations of the PCR process have been developed, including quantitative PCR (qPCR) for monitoring DNA amplification in real-time and reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) for the detection of RNA, a tool that has become instrumental in viral diagnostics.
Reverse-Transcription PCR
Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a highly sensitive technique for the detection and quantitation of mRNA expression levels. In RT-PCR, the RNA template is reverse transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA), using reverse transcriptase. The cDNA is then used as a template for exponential amplification using standard PCR procedure (denaturation, annealing, and elongation). RT-PCR is used in various applications, including gene expression analysis, microarray validation, pathogen detection, and disease research.
Quantitative PCR
Quantitative or real-time PCR (qPCR) enables researchers to monitor the amplification of a DNA template in real-time and not at its end-point, as in conventional PCR. It does so using fluorescent reporter molecules which bind to and detect products generated during each cycle of the PCR process. As the reaction proceeds, fluorescence increases due to the accumulation of the PCR product with each amplification cycle. These fluorescent reporter molecules include dyes that bind to the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), such as Helixyte™ Green (Cat No. 17591) and Q4ever™ Green (Cat No. 17608), or fluorescently labeled sequence-specific probes, such as TaqMan® probes, Molecular Beacons and Scorpion® probes.
Dye-Based qPCR
In qPCR, dsDNA binding dyes are frequently used as fluorescent reporters to measure gene expression. The fluorescence of the reporter dye increases as the product accumulates with each successive cycle of amplification. Recording the amount of fluorescence emission at each cycle makes it possible to monitor the PCR reaction during the exponential phase. Compared to microarrays, qPCR is more sensitive at detecting modest changes in expression levels, making it well-suited for investigating small subsets of genes. Although dsDNA-binding dyes provide the most convenient and cheapest option for qPCR, the principal drawback to intercalation-based detection of PCR product accumulation is that both specific and nonspecific products generate signals.
qPCR using Helixyte™ Green (Cat No. 17591). During the extension phase, DNA polymerase extends the sequence-specific primer by incorporating dNTPs complementary to the DNA template. As newly synthesized double-stranded DNA is produced, Helixyte™ Green will bind to the DNA complexes and fluoresce (figure made in BioRender).
Table 3. Double-stranded DNA-binding dyes for qPCR
| Product ▲ ▼ | Ex (nm) ▲ ▼ | Em (nm) ▲ ▼ | Unit Size ▲ ▼ | Cat No. ▲ ▼ |
| Helixyte™ Green *20X Aqueous PCR Solution* | 498 nm | 522 nm | 5x1 mL | 17591 |
| Helixyte™ Green *10,000X Aqueous PCR Solution* | 498 nm | 522 nm | 1 mL | 17592 |
| Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent *200X DMSO Solution* | 490 nm | 525 nm | 1 mL | 17597 |
| Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent *200X DMSO Solution* | 490 nm | 525 nm | 10 mL | 17598 |
| Q4ever™ Green *1250X DMSO Solution* | 503 nm | 527 nm | 100 µL | 17608 |
| Q4ever™ Green *1250X DMSO Solution* | 503 nm | 527 nm | 2 mL | 17609 |
Probe-Based qPCR
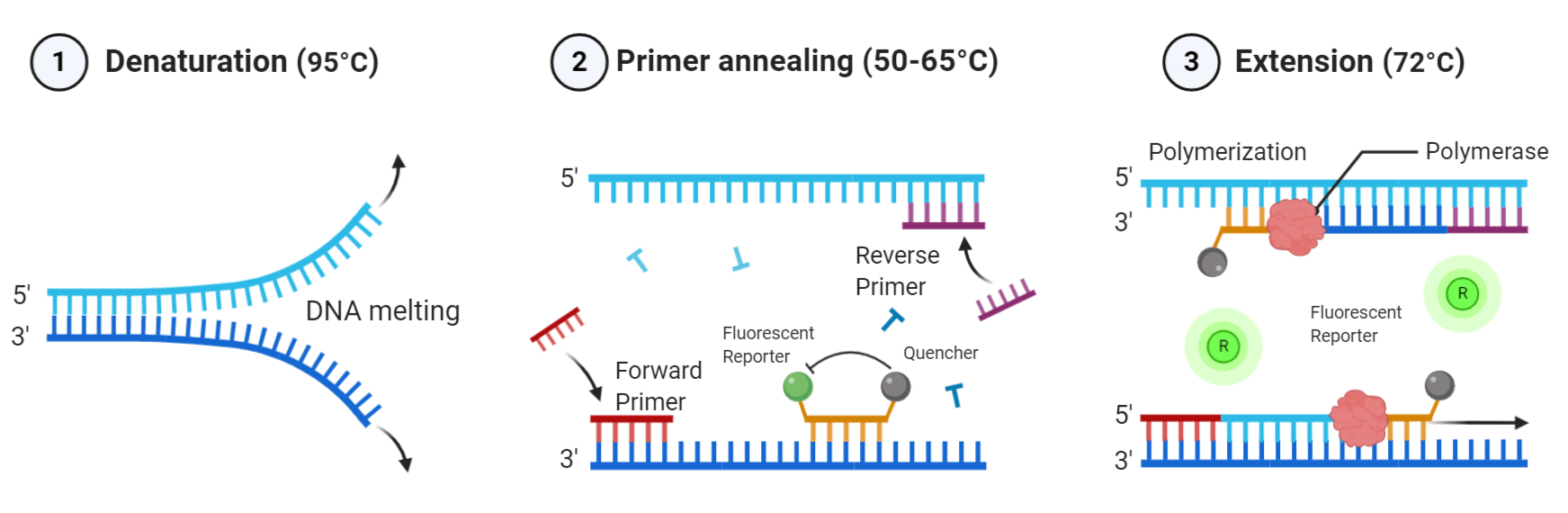
Probe-based qPCR utilizes target-specific probes to precisely measure DNA amplification at each cycle of the PCR reaction. While probe designs may vary, they typically share three key elements: a short oligonucleotide that is complementary to the target sequence, a fluorescent reporter dye-labeled to the 5' end, and a quencher dye on the 3' end (for information on recommended FRET pairs, see table below). Due to the biochemical phenomenon known as Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), the fluorescence of the reporter dye is masked by the quencher dye while the probe remains intact. As DNA polymerase extends the primer during elongation, it also hydrolyzes sequence-specific probes that have annealed to the single-stranded DNA template, separating the reporter dye from the quencher and resulting in an amplification-dependent increase in fluorescence. Probe-based qPCR is a favorable method beneficial for specific hybridization, no false positives, and multiplex analysis of multiple target sequences in a single reaction tube.
Illustration of probe-based qPCR. As DNA polymerase extends the primer during elongation, it hydrolyzes sequence-specific probes that have annealed to the single-stranded DNA template, separating the reporter dye from the quencher and resulting in an amplification-dependent increase in fluorescence (figure made in BioRender).
Table 4. Fluorescent reporter dyes for labeling the 5' end or 3' end on sequence-specific qPCR probes.
| Product ▲ ▼ | Ex (nm) ▲ ▼ | Em (nm) ▲ ▼ | Unit Size ▲ ▼ | Cat No. ▲ ▼ |
| EDANS acid [5-((2-Aminoethyl)amino)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid] *CAS 50402-56-7* | 336 | 455 | 1 g | 610 |
| EDANS acid [5-((2-Aminoethyl)amino)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid] *CAS 50402-56-7* | 336 | 455 | 10 g | 611 |
| EDANS C5 maleimide | 336 | 455 | 5 mg | 619 |
| EDANS sodium salt [5-((2-Aminoethyl)aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid, sodium salt] *CAS 100900-07-0* | 336 | 455 | 1 g | 615 |
| EDANS sodium salt [5-((2-Aminoethyl)aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid, sodium salt] *CAS 100900-07-0* | 336 | 455 | 10 g | 616 |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 acid [TF1 acid] *Superior replacement for EDANS* | 341 | 448 | 100 mg | 2238 |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 alkyne [TF1 alkyne] | 341 | 448 | 5 mg | 2237 |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 amine [TF1 amine] *Superior replacement for EDANS* | 341 | 448 | 5 mg | 2239 |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 azide [TF1 azide] | 341 | 448 | 5 mg | 2236 |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 CPG [TF1 CPG] *500 Å* | 341 | 448 | 100 mg | 2240 |
Table 5. Quencher dyes for labeling the 5' end or 3' end on sequence-specific qPCR probes.
| Product ▲ ▼ | Ex (nm) ▲ ▼ | Em (nm) ▲ ▼ | Unit Size ▲ ▼ | Cat No. ▲ ▼ |
| DABCYL acid [4-((4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)benzoic acid] *CAS 6268-49-1* | 454 | N/A | 5 g | 2001 |
| DABCYL C2 amine | 454 | N/A | 100 mg | 2006 |
| DABCYL C2 maleimide | 454 | N/A | 25 mg | 2008 |
| DABCYL-DBCO | 454 | N/A | 5 mg | 2010 |
| DABCYL succinimidyl ester [4-((4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)benzoic acid, succinimidyl ester] *CAS 146998-31-4* | 454 | N/A | 1 g | 2004 |
| DABCYL succinimidyl ester [4-((4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)benzoic acid, succinimidyl ester] *CAS 146998-31-4* | 454 | N/A | 5 g | 2005 |
| 3'-DABCYL CPG *1000 Å* | 454 | N/A | 1 g | 6008 |
| 5'-DABCYL C6 Phosphoramidite | 454 | N/A | 1 g | 6009 |
| Tide Quencher™ 1 acid [TQ1 acid] | 492 | N/A | 100 mg | 2190 |
| Tide Quencher™ 1 alkyne [TQ1 alkyne] | 492 | N/A | 5 mg | 2189 |
Additional Resources
Recommended FRET Pairs
Table 6. Recommended FRET pairs for developing FRET oligonucleotides
| Donor \ Acceptor ▲ ▼ | DABCYL ▲ ▼ | TQ1 ▲ ▼ | TQ2 ▲ ▼ | TQ3 ▲ ▼ | TQ4 ▲ ▼ | TQ5 ▲ ▼ | TQ6 ▲ ▼ | TQ7 ▲ ▼ |
| EDANS | +++ | +++ | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| MCA | +++ | +++ | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tide Fluor™ 1 | +++ | +++ | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| FAM FITC | + | + | +++ | + | - | - | - | - |
| Cy2® Tide Fluor™ 2 | + | + | +++ | + | - | - | - | - |
| HEX JOE TET | - | - | + | +++ | + | - | - | - |
| Cy3® TAMRA Tide Fluor™ 3 | - | - | + | +++ | + | - | - | - |
| ROX Texas Red® | - | - | - | + | +++ | + | - | - |
| Tide Fluor™ 4 | - | - | - | + | +++ | + | - | - |
| Cy5® Tide Fluor™ 5 | - | - | - | - | + | +++ | + | - |
ROX Reference and Reporter Dye Combinations
Table 7. Possible ROX Reference and reporter dye combinations for multiplex qPCR assays.
| Instrument ▲ ▼ | Reference Dye ▲ ▼ | Reporter Dye 1 ▲ ▼ | Reporter Dye 2 ▲ ▼ | Reporter Dye 3 ▲ ▼ | Reporter Dye 4 ▲ ▼ |
| ABI PRISM® 7700 | ROX | 6-FAM | 6-TET | - | - |
| ABI PRISM® 7000 and 7900 Applied Biosystems® 7300 StepOnePlus™ | ROX | 6-FAM | 6-TET | 6-HEX | - |
| Applied Biosystems® 7500 | ROX | 6-FAM | 6-TET | 6-HEX | Tide Fluor™ 3 iFluor® 647 Alexa Fluor 647 Cy5 |